Structural definition of hSP-D recognition of Salmonella enterica LPS inner core oligosaccharides reveals alternative binding modes for the same LPS
- PMID: 29912941
- PMCID: PMC6005524
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199175
Structural definition of hSP-D recognition of Salmonella enterica LPS inner core oligosaccharides reveals alternative binding modes for the same LPS
Abstract
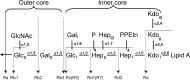
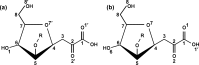
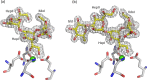
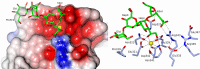
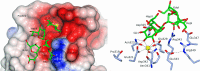
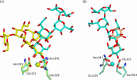
The crystal structures of a biologically and therapeutically active recombinant homotrimeric fragment of native human SP-D (hSP-D) complexed with the inner core oligosaccharide of the Salmonella enterica sv Minnesota rough strains R5 and R7 (rough mutant chemotypes Rc and Rd1) have been determined. The structures reveal that hSP-D specifically and preferentially targets the LPS inner core via the innermost conserved Hep-Kdo pair with the flexibility for alternative recognition when this preferred epitope is not available for binding. Hep-Kdo binding is achieved through calcium dependent recognition of the heptose dihydroxyethyl side chain coupled with specific interactions between the Kdo and the binding site flanking residues Arg343 and Asp325 with evidence for an extended binding site for LPS inner cores containing multiple Kdo residues. In one subunit of the R5-bound structure this preferred mode of binding is precluded by the crystal lattice and oligosaccharide is bound through the terminal inner core glucose. The structures presented here thus provide unique multiple insights into the recognition and binding of bacterial LPS by hSP-D. Not only is it demonstrated that hSP-D targets the highly conserved LPS proximal inner core Hep-Kdo motif, but also that hSP-D can recognise either terminal or non-terminal sugars and has the flexibility and versatility to adopt alternative strategies for bacterial recognition, utilising alternative LPS epitopes when the preferred inner core Hep-Kdo disaccharide is not available for binding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
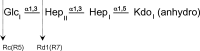

References
-
- Ujma S, Horsnell WGC, Katz A, Clark HW, Schäfer G. Non-Pulmonary Immune Functions of Surfactant Proteins A and D. J Innate Immun. 2017;9:3–11. doi: 10.1159/000451026 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reid KBM. Interactions of surfactant protein D with pathogens, allergens and phagocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998;1408:290–5. - PubMed
-
- LeVine AM, Whitsett JA. Pulmonary collectins and innate host defense of the lung. Microbes Infect. 2001;3:161–6. - PubMed
-
- Crouch EC, Wright JR. Surfactant proteins A and D and pulmonary host defence. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:521–4. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.521 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Madan T, Kishore U, Singh M, Strong P, Clark HW, Hussain EM et al. Surfactant proteins A and D protect mice against pulmonary hypersensitivity induced by Aspergillus fumigatus antigens and allergens. J Clin Invest. 2001;107:467–75. doi: 10.1172/JCI10124 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

