The blue mussel Mytilus edulis is vulnerable to the toxic dinoflagellate Karlodinium armiger-Adult filtration is inhibited and several life stages killed
- PMID: 29912948
- PMCID: PMC6005564
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199306
The blue mussel Mytilus edulis is vulnerable to the toxic dinoflagellate Karlodinium armiger-Adult filtration is inhibited and several life stages killed
Abstract
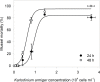
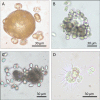
Blooms of the toxic dinoflagellates Karlodinium armiger and K. veneficum are frequently observed in Alfacs Bay, Spain, causing mass mortality to wild and farmed mussels. An isolate of K. armiger from Alfacs Bay was grown in the laboratory and exposed to adults, embryos and trochophore larvae of the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis. Adult mussels rejected to filter K. armiger at cell concentrations >1.5·103 cells ml-1. Exposure of adult mussels (23-33 mm shell length) to a range of K. armiger cell concentrations led to mussel mortality with LC50 values of 9.4·103 and 6.1·103 cells ml-1 after 24 and 48 h exposure to ~3.6·104 K. armiger cells ml-1, respectively. Karlodinium armiger also affected mussel embryos and trochophore larvae and feeding by K. armiger on both embryos and larvae was observed under the microscope. Embryos exposed to low K. armiger cell concentrations suffered no measurable mortality. However, at higher K. armiger cell concentrations the mortality of the embryos increased significantly with cell concentration and reached 97% at 1.8·103 K. armiger cells ml-1 after 29 h of exposure. Natural K. armiger blooms may not only have serious direct effects on benthic communities, but may also affect the recruitment of mussels in affected areas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Garcés E. In situ growth rate and distribution of the ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium corsicum Paulmier in an estuarine embayment (Alfacs Bay, NW Mediterranean Sea). J Plankton Res. 1999;21: 1977–1991. doi: 10.1093/plankt/21.10.1977 - DOI
-
- Garcés E, Fernández-Tejedor M, Penna A, Van Lenning K, Gutierrez A, Camp J, et al. Characterization of nw mediterranean Karlodinium spp. (Dinophyceae) strains using morphological, molecular, chemical, and physiological methodologies. J Phycol. 2006;42: 1096–1112. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8817.2006.00270.x - DOI
-
- Fernández-Tejedor M, Delgado M, Garcés E, Camp J, Diogène J. Toxic phytoplankton response to warming in two Mediterranean bays of the Ebro Delta. CIESM Work Monogr Phytoplankt Response to Mediterr Environ Chang No 40. 2010; 83–88.
-
- Guallar C, Delgado M, Diogène J, Fernández-Tejedor M. Artificial neural network approach to population dynamics of harmful algal blooms in Alfacs Bay (NW Mediterranean): Case studies of Karlodinium and Pseudo-nitzschia. Ecol Modell. Elsevier B.V.; 2016;338: 37–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2016.07.009 - DOI
-
- Place AR, Bowers HA, Bachvaroff TR, Adolf JE, Deeds JR, Sheng J. Karlodinium veneficum-The little dinoflagellate with a big bite. Harmful Algae. Elsevier B.V.; 2012;14: 179–195. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2011.10.021 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

