Tongxinluo attenuates reperfusion injury in diabetic hearts by angiopoietin-like 4-mediated protection of endothelial barrier integrity via PPAR-α pathway
- PMID: 29912977
- PMCID: PMC6005559
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198403
Tongxinluo attenuates reperfusion injury in diabetic hearts by angiopoietin-like 4-mediated protection of endothelial barrier integrity via PPAR-α pathway
Abstract
Objective: Endothelial barrier function in the onset and Tongxinluo (TXL) protection of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, and TXL can induce the secretion of Angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4) in human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells during hypoxia/reoxygenation. We intend to demonstrate whether TXL can attenuate myocardial I/R injury in diabetes, characterized with microvascular endothelial barrier disruption, by induction of Angptl4-mediated protection of endothelial barrier integrity.
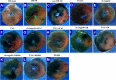
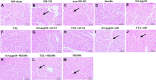
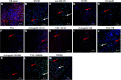
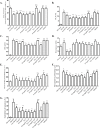
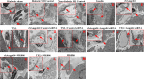
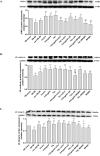
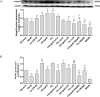
Methods and results: I/R injury was created by coronary ligation in ZDF diabetic and non-diabetic control rats. The animals were anesthetized and randomized to sham operation or I/R injury with or without the exposure to insulin, rhAngptl4, TXL, Angptl4 siRNA, and the PPAR-α inhibitor MK886. Tongxinluo, insulin and rhAngptl4 have the similar protective effect on diabetic hearts against I/R injury. In I/R-injured diabetic hearts, TXL treatment remarkably reduced the infarct size, and protected endothelial barrier integrity demonstrated by decreased endothelial cells apoptosis, microvascular permeability, and myocardial hemorrhage, fortified tight junction, and upregulated expression of JAM-A, integrin-α5, and VE-cadherin, and these effects of TXL were as effective as insulin and rhAngptl4. However, Angptl4 knock-down with siRNA interference and inhibition of PPAR-α with MK886 partially diminished these beneficial effects of TXL and rhAngptl4. TXL induced the expression of Angptl4 in I/R-injured diabetic hearts, and was canceled by Angptl4 siRNA and MK886. TXL treatment increased myocardial PPAR-α activity, and was abolished by MK886 but not by Angptl4 siRNA.
Conclusions: TXL protects diabetic hearts against I/R injury by activating Angptl4-mediated restoration of endothelial barrier integrity via the PPAR-α pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hillis LD, Lange RA (2006) Myocardial infarction and the open-artery hypothesis. N Engl J Med 355: 2475–2477. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe068251 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Liu Y, Lu XT, Wu YL, Zhang C, Ji XP, et al. (2009) Traditional Chinese medication Tongxinluo dose-dependently enhances stability of vulnerable plaques: a comparison with a high-dose simvastatin therapy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297: H2004–2014. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00208.2009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li XD, Yang YJ, Geng YJ, Jin C, Hu FH, Zhao JL, et al. (2010) Tongxinluo reduces myocardial no-reflow and ischemia-reperfusion injury by stimulating the phosphorylation of eNOS via the PKA pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 299: H1255–1261. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00459.2010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cheng YT, Yang YJ, Zhang HT, Qian HY, Zhao JL, Meng XM, et al. (2009) Pretreatment with Tongxinluo protects porcine myocardium from ischaemia/reperfusion injury through a nitric oxide related mechanism. Chin Med J (Engl) 122: 1529–1538. - PubMed
-
- Li XD, Yang YJ, Cheng YT, Dou KF, Tian Y, Meng XM (2013) Protein kinase A-mediated cardioprotection of Tongxinluo relates to the inhibition of myocardial inflammation, apoptosis, and edema in reperfused swine hearts. Chin Med J (Engl) 126: 1469–1479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

