Discovery of a novel potent peptide agonist to adiponectin receptor 1
- PMID: 29912982
- PMCID: PMC6005460
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199256
Discovery of a novel potent peptide agonist to adiponectin receptor 1
Abstract
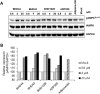
Activation of adiponectin receptors (AdipoRs) by its natural ligand, adiponectin has been known to be involved in modulating critical metabolic processes such as glucose metabolism and fatty acid oxidation as demonstrated by a number of in vitro and in vivo studies over last two decades. These findings suggest that AdipoRs' agonists could be developed into a potential therapeutic agent for metabolic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, especially for type II diabetes, a long-term metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Because of limitations in production of biologically active adiponectin, adiponectin-mimetic AdipoRs' agonists have been suggested as alternative ways to expand the opportunity to develop anti-diabetic agents. Based on crystal structure of AdipoR1, we designed AdipoR1's peptide agonists using protein-peptide docking simulation and screened their receptor binding abilities and biological functions via surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and biological analysis. Three candidate peptides, BHD1028, BHD43, and BHD44 were selected and confirmed to activate AdipoR1-mediated signal pathways. In order to enhance the stability and solubility of peptide agonists, candidate peptides were PEGylated. PEGylated BHD1028 exhibited its biological activity at nano-molar concentration and could be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetes. Also, SPR and virtual screening techniques utilized in this study may potentially be applied to other peptide-drug screening processes against membrane receptor proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
B.B.K. is a salaried employee of EncuraGen, S.K. is a salaried employee of Polus Inc., and Y.J.S. is a salaried employee of Samhyun Inc. With regards to the patent related to the submission, there is a registered patent in Korea. The patent number is 10-1838622 and the title is Agonist Peptide for Adiponectin Receptor. Also, a PCT application was filed as of April 10, 2017 and the application number is 10-2017-0037762. This does not alter the authors' adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
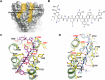




Similar articles
-
PEG-BHD1028 Peptide Regulates Insulin Resistance and Fatty Acid β-Oxidation, and Mitochondrial Biogenesis by Binding to Two Heterogeneous Binding Sites of Adiponectin Receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 17;22(2):884. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020884. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33477324 Free PMC article.
-
Orally active osteoanabolic agent GTDF binds to adiponectin receptors, with a preference for AdipoR1, induces adiponectin-associated signaling, and improves metabolic health in a rodent model of diabetes.Diabetes. 2014 Oct;63(10):3530-44. doi: 10.2337/db13-1619. Epub 2014 May 21. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24848063
-
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae assay system to investigate ligand/AdipoR1 interactions that lead to cellular signaling.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 7;8(6):e65454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065454. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762377 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin receptors: a review of their structure, function and how they work.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Jan;28(1):15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 15. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24417942 Review.
-
Physiological and pathophysiological roles of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in the integrated regulation of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Dec;32 Suppl 7:S13-8. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.233. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. PMID: 19136982 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Adiponectin in Breast Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 17;10(11):2958. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112958. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36428526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin and Its Mimics on Skeletal Muscle: Insulin Sensitizers, Fat Burners, Exercise Mimickers, Muscling Pills … or Everything Together?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 9;21(7):2620. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072620. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32283840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PEG-BHD1028 Peptide Regulates Insulin Resistance and Fatty Acid β-Oxidation, and Mitochondrial Biogenesis by Binding to Two Heterogeneous Binding Sites of Adiponectin Receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 17;22(2):884. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020884. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33477324 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of bioassay and non-target metabolite analysis of tomato reveals that β-carotene and lycopene activate the adiponectin signaling pathway, including AMPK phosphorylation.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 1;17(7):e0267248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267248. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35776737 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Role of Adiponectin Receptors in Obesity-Related Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 17;24(10):8907. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108907. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240258 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi Y, Hu FB. The global implications of diabetes and cancer. Lancet. 2014;383(9933):1947–8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60886-2 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holland WL, Scherer PE. Cell Biology. Ronning after the adiponectin receptors. Science. 2013;342(6165):1460–1. doi: 10.1126/science.1249077 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4084614. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K, Ueki K, Tobe K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(7):1784–92. doi: 10.1172/JCI29126 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC1483172. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iwabu M, Yamauchi T, Okada-Iwabu M, Sato K, Nakagawa T, Funata M, et al. Adiponectin and AdipoR1 regulate PGC-1alpha and mitochondria by Ca(2+) and AMPK/SIRT1. Nature. 2010;464(7293):1313–9. doi: 10.1038/nature08991 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med. 2002;8(11):1288–95. doi: 10.1038/nm788 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

