Formin proteins in megakaryocytes and platelets: regulation of actin and microtubule dynamics
- PMID: 29913076
- PMCID: PMC6406210
- DOI: 10.1080/09537104.2018.1481937
Formin proteins in megakaryocytes and platelets: regulation of actin and microtubule dynamics
Abstract
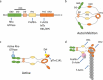
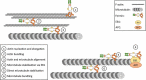
The platelet and megakaryocyte cytoskeletons are essential for formation and function of these cells. A dynamic, properly organised tubulin and actin cytoskeleton is critical for the development of the megakaryocyte and the extension of proplatelets. Tubulin in particular plays a pivotal role in the extension of these proplatelets and the release of platelets from them. Tubulin is further required for the maintenance of platelet size, and actin is the driving force for shape change, spreading and platelet contraction during platelet activation. Whilst several key proteins which regulate these cytoskeletons have been described in detail, the formin family of proteins has received less attention. Formins are intriguing as, although they were initially believed to simply be a nucleator of actin polymerisation, increasing evidence shows they are important regulators of the crosstalk between the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons. In this review, we will introduce the formin proteins and consider the recent evidence that they play an important role in platelets and megakaryocytes in mediating both the actin and tubulin cytoskeletons.
Keywords: Actin; Formin; macrothrombocytopenia; microtubules cytoskeleton; proplatelet formation.
Figures
References
-
- Castrillon DH, Wasserman SA. Diaphanous is required for cytokinesis in Drosophila and shares domains of similarity with the products of the limb deformity gene. Development. 1994;120:3367–3377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
