Anticoagulant Activities of Indobufen, an Antiplatelet Drug
- PMID: 29914049
- PMCID: PMC6099839
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23061452
Anticoagulant Activities of Indobufen, an Antiplatelet Drug
Abstract
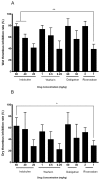
Indobufen is a new generation of anti-platelet aggregation drug, but studies were not sufficient on its anticoagulant effects. In the present study, the anticoagulant activity of indobufen was determined by monitoring the activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), and thrombin time (TT) in rabbit plasma. We evaluated the anticoagulant mechanisms on the content of the platelet factor 3,4 (PF3,4), and the coagulation factor 1, 2, 5, 8, 10 (FI, II, V, VIII, X) in rabbits, as well as the in vivo bleeding time and clotting time in mice. The pharmacodynamic differences between indobufen and warfarin sodium, rivaroxaban, and dabigatran were further studied on thrombus formation and the content of FII and FX in rats. Animal experiments showed that intragastric-administrated indobufen can significantly reduce the APTT, PT, TT, PF3, FI, II, V, VIII, and X plasma contents. Its inhibitory effect on plasma FII was better than thrombin inhibitor dabigatran with effect on FX better than FXa inhibitor rivaroxaban. These results suggest that indobufen has some anticoagulant effects as strong as some conventional anticoagulants. The mechanism may be related to both exogenous and endogenous coagulation system.
Keywords: anticoagulant effect; coagulation factor; indobufen; platelet factor..
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Butenas S., Mann K.G. Blood coagulation. Biochemistry. 2002;67:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Prevention T.S. The italian guidelines for stroke prevention. Neurol. Sci. 2000;21:5–12. - PubMed
-
- Schuijt T.J., Bakhtiari K., Daffre S., Deponte K., Wielders S.J., Marquart J.A., Hovius J.W., van der Poll T., Fikrig E., Bunce M.W., et al. Factor Xa activation of factor V is of paramount importance in initiating the coagulation system: Lessons from a tick salivary protein. Circulation. 2013;128:254–266. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003191. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

