Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis
- PMID: 29914056
- PMCID: PMC6025611
- DOI: 10.3390/cells7060060
Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Yap et al. Real-Time Imaging of Retinal Ganglion Cell Apoptosis. Cells 2018, 7, 60.Cells. 2025 Oct 28;14(21):1690. doi: 10.3390/cells14211690. Cells. 2025. PMID: 41227391 Free PMC article.
Abstract
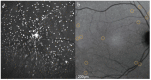
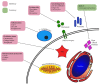
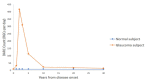
Monitoring real-time apoptosis in-vivo is an unmet need of neurodegeneration science, both in clinical and research settings. For patients, earlier diagnosis before the onset of symptoms provides a window of time in which to instigate treatment. For researchers, being able to objectively monitor the rates of underlying degenerative processes at a cellular level provides a biomarker with which to test novel therapeutics. The DARC (Detection of Apoptosing Retinal Cells) project has developed a minimally invasive method using fluorescent annexin A5 to detect rates of apoptosis in retinal ganglion cells, the key pathological process in glaucoma. Numerous animal studies have used DARC to show efficacy of novel, pressure-independent treatment strategies in models of glaucoma and other conditions where retinal apoptosis is reported, including Alzheimer’s disease. This may forge exciting new links in the clinical science of treating both cognitive and visual decline. Human trials are now underway, successfully demonstrating the safety and efficacy of the technique to differentiate patients with progressive neurodegeneration from healthy individuals. We review the current perspectives on retinal ganglion cell apoptosis, the way in which this can be imaged, and the exciting advantages that these future methods hold in store.
Keywords: annexin; apoptosis; glaucoma; imaging; neurodegeneration; retinal ganglion cell.
Conflict of interest statement
M.F.C. is a named co-inventor on granted patent EP 2231199B1 and published patent WO 2011055121 A1 owned by UCL and related to DARC technology. The other authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

