Functionalized Tyrosinase-Lignin Nanoparticles as Sustainable Catalysts for the Oxidation of Phenols
- PMID: 29914085
- PMCID: PMC6027214
- DOI: 10.3390/nano8060438
Functionalized Tyrosinase-Lignin Nanoparticles as Sustainable Catalysts for the Oxidation of Phenols
Abstract
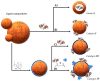
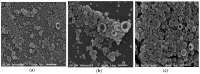
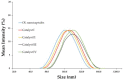
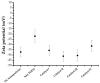
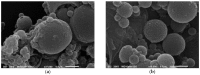
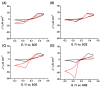
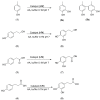
Sustainable catalysts for the oxidation of phenol derivatives under environmentally friendly conditions were prepared by the functionalization of lignin nanoparticles with tyrosinase. Lignin, the most abundant polyphenol in nature, is the main byproduct in the pulp and paper manufacturing industry and biorefinery. Tyrosinase has been immobilized by direct adsorption, encapsulation, and layer-by-layer deposition, with or without glutaraldehyde reticulation. Lignin nanoparticles were found to be stable to the tyrosinase activity. After the enzyme immobilization, they showed a moderate to high catalytic effect in the synthesis of catechol derivatives, with the efficacy of the catalyst being dependent on the specific immobilization procedures.
Keywords: lignin nanoparticles; oxidation of phenols; sustainable catalyst; tyrosinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ghisellini P., Cialani C., Ulgiati S. A review on circular economy: The expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2016;114:11–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.007. - DOI
-
- Hu T.Q., editor. Chemical Modification, Properties, and Usage of Lignin. Kluwer Academic-Plenum Publishers; New York, NY, USA: 2002.
-
- Kaur R., Uppal S.K. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of lignin from sugarcane bagasse. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015;293:2585–2592. doi: 10.1007/s00396-015-3653-1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

