Macrodiscs Comprising SMALPs for Oriented Sample Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy of Membrane Proteins
- PMID: 29914645
- PMCID: PMC6035293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.05.024
Macrodiscs Comprising SMALPs for Oriented Sample Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy of Membrane Proteins
Abstract
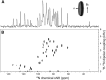
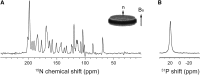
Macrodiscs, which are magnetically alignable lipid bilayer discs with diameters of >30 nm, were obtained by solubilizing protein-containing liposomes with styrene-maleic acid copolymers. Macrodiscs provide a detergent-free phospholipid bilayer environment for biophysical and functional studies of membrane proteins under physiological conditions. The narrow resonance linewidths observed from membrane proteins in styrene-maleic acid macrodiscs advance structure determination by oriented sample solid-state NMR spectroscopy.
Copyright © 2018 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Wang S., Ladizhansky V. Recent advances in magic angle spinning solid state NMR of membrane proteins. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2014;82:1–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

