Zinc Metallochaperones Reactivate Mutant p53 Using an ON/OFF Switch Mechanism: A New Paradigm in Cancer Therapeutics
- PMID: 29914895
- PMCID: PMC6139040
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0822
Zinc Metallochaperones Reactivate Mutant p53 Using an ON/OFF Switch Mechanism: A New Paradigm in Cancer Therapeutics
Abstract
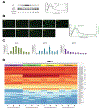
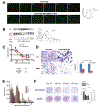
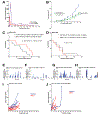
Purpose: Zinc metallochaperones (ZMC) are a new class of anticancer drugs that reactivate zinc-deficient mutant p53 by raising and buffering intracellular zinc levels sufficiently to restore zinc binding. In vitro pharmacodynamics of ZMCs indicate that p53-mutant activity is ON by 4-6 hours and is OFF by 24. We sought to understand the mechanism of this regulation and to translate these findings preclinically. We further sought to innovate the formulation of ZMCs to improve efficacy.Experimental Design: We performed in vitro mechanistic studies to determine the role of cellular zinc homeostatic mechanisms in the transient pharmacodynamics of ZMCs. We conducted preclinical pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and efficacy studies using a genetically engineered murine pancreatic cancer model (KPC) to translate these mechanistic findings and investigate a novel ZMC formulation.Results:In vitro, cellular zinc homeostatic mechanisms that restore zinc to its physiologic levels function as the OFF switch in ZMC pharmacodynamics. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies indicate that ZMCs have a short half-life (< 30 minutes), which is sufficient to significantly improve survival in mice expressing a zinc-deficient allele (p53R172H) while having no effect in mice expressing a non-zinc-deficient allele (p53R270H). We synthesized a novel formulation of the drug in complex with zinc and demonstrate this significantly improves survival over ZMC1.Conclusions: Cellular zinc homeostatic mechanisms function as an OFF switch in ZMC pharmacodynamics, indicating that a brief period of p53-mutant reactivation is sufficient for on-target efficacy. ZMCs synthesized in complex with zinc are an improved formulation. Clin Cancer Res; 24(18); 4505-17. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Zinc Metallochaperones as Mutant p53 Reactivators: A New Paradigm in Cancer Therapeutics.Cancers (Basel). 2018 May 29;10(6):166. doi: 10.3390/cancers10060166. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29843463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial Therapy of Zinc Metallochaperones with Mutant p53 Reactivation and Diminished Copper Binding.Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Aug;18(8):1355-1365. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-1080. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Mol Cancer Ther. 2019. PMID: 31196889 Free PMC article.
-
Thiosemicarbazones Functioning as Zinc Metallochaperones to Reactivate Mutant p53.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;91(6):567-575. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.107409. Epub 2017 Mar 20. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28320780 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of BRCA1 and TP53 mutant breast cancer through mutant p53 reactivation.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2019 Apr 15;5:14. doi: 10.1038/s41523-019-0110-1. eCollection 2019. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30993195 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivating mutant p53 using small molecules as zinc metallochaperones: awakening a sleeping giant in cancer.Drug Discov Today. 2015 Nov;20(11):1391-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Drug Discov Today. 2015. PMID: 26205328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A thiol-bound drug reservoir enhances APR-246-induced mutant p53 tumor cell death.EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Feb 5;13(2):e10852. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201910852. Epub 2020 Dec 14. EMBO Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33314700 Free PMC article.
-
Salvation of the fallen angel: Reactivating mutant p53.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Apr;176(7):817-831. doi: 10.1111/bph.14572. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30632144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limited nutrient availability in the tumor microenvironment renders pancreatic tumors sensitive to allosteric IDH1 inhibitors.Nat Cancer. 2022 Jul;3(7):852-865. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00393-y. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Nat Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35681100 Free PMC article.
-
A role for bioinorganic chemistry in the reactivation of mutant p53 in cancer.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2022 Aug;27(4-5):393-403. doi: 10.1007/s00775-022-01939-2. Epub 2022 Apr 30. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35488931 Review.
-
Integrated stress response (ISR) activation and apoptosis through HRI kinase by PG3 and other p53 pathway-restoring cancer therapeutics.Oncotarget. 2024 Sep 17;15:614-633. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28637. Oncotarget. 2024. PMID: 39288289 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

