Early BCR-ABL1 decline in imatinib-treated patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: results from a multicenter study of the Chinese CML alliance
- PMID: 29915172
- PMCID: PMC6006175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-018-0093-4
Early BCR-ABL1 decline in imatinib-treated patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: results from a multicenter study of the Chinese CML alliance
Abstract
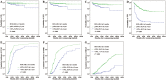
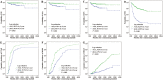
An early molecular response is spectacularly predictive of outcome in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and early response landmarks may identify the high-risk patients likely to be benefit from an early therapy switch. In this study, we evaluated the most relevant cutoffs for early molecular response markers (BCR-ABL1 values at 3 months, log reduction and halving time between diagnosis and 3 months) in 476 first-line imatinib-treated Chinese patients with chronic phase CML. All outcomes were significantly superior for the 324 patients with 3-month BCR-ABL1 ≤10%, so did for the 270 patients with BCR-ABL1 >0.61 log reduction. BCR-ABL1 halving time ≤22 days was identified for patients with the most favorable outcome. Moreover, the prognosis was significantly poorest for patients with both halving time >44 days and BCR-ABL1 >10%. Importantly, multivariate regression analysis demonstrated that a BCR-ABL1 log reduction calculated at 3 months of 0.61 was the only variable that significantly predicted for OS. Our results highlight the importance of rapid initial decline of BCR-ABL1 in predicting satisfactory outcome. Our data support the evidence that monitoring BCR-ABL1 values at an early time point could contribute to accurately assess response and ultimately guide clinical decisions regarding the timing of therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Early BCR-ABL1 Reduction Is Predictive of Better Event-free Survival in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated With Any Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016 Aug;16 Suppl:S96-S100. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2016.03.008. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016. PMID: 27131622 Review.
-
The BCR-ABL1 transcript type influences response and outcome in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated frontline with imatinib.Am J Hematol. 2017 Aug;92(8):797-805. doi: 10.1002/ajh.24774. Epub 2017 May 30. Am J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28466557
-
Clinical Implications of Discordant Early Molecular Responses in CML Patients Treated with Imatinib.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 6;20(9):2226. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092226. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31064152 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of second decline rate of BCR-ABL1 transcript on clinical outcome of chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients on imatinib first-line.Ann Hematol. 2019 May;98(5):1159-1168. doi: 10.1007/s00277-019-03633-x. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Ann Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30798348
-
Initial treatment for patients with CML.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009:453-60. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2009.1.453. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009. PMID: 20008231 Review.
Cited by
-
BCR-ABL1 transcript decline ratio combined BCR-ABL1IS as a precise predictor for imatinib response and outcome in the patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.J Cancer. 2020 Feb 3;11(8):2234-2240. doi: 10.7150/jca.38752. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32127950 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of first-line nilotinib therapy and evaluation of the clinical utility of the FRET-based drug sensitivity test.Int J Hematol. 2019 Oct;110(4):482-489. doi: 10.1007/s12185-019-02696-w. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Int J Hematol. 2019. PMID: 31240558 Clinical Trial.
-
Predictive Factors for Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Reduction Ratio and Halving Time of BCR::ABL1 IS Transcript Levels.Turk J Haematol. 2022 Aug 25;39(3):196-203. doi: 10.4274/tjh.galenos.2022.2022-0024. Epub 2022 May 27. Turk J Haematol. 2022. PMID: 35620443 Free PMC article.
-
Kinome-Wide siRNA Screening Identifies DYRK1B as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 18;13(22):5779. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225779. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fujisawa S, et al. Efficacy and safety of dasatinib versus imatinib in Japanese patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML-CP): subset analysis of the DASISION trial with 2-year follow-up. Int. J. Hematol. 2014;99:141–153. doi: 10.1007/s12185-013-1470-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

