BMP and WNT signalling cooperate through LEF1 in the neuronal specification of adult hippocampal neural stem and progenitor cells
- PMID: 29915186
- PMCID: PMC6006330
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27581-0
BMP and WNT signalling cooperate through LEF1 in the neuronal specification of adult hippocampal neural stem and progenitor cells
Abstract
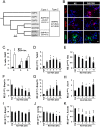
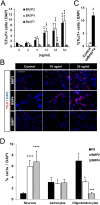
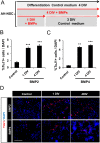
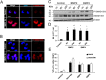
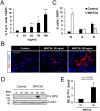
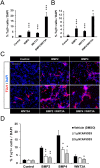
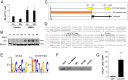
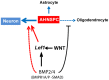
Neuronal production from neural stem cells persists during adulthood in the subgranular zone of the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Extracellular signals provided by the hippocampal microenvironment regulate the neuronal fate commitment of the stem cell progeny. To date, the identity of those signals and their crosstalk has been only partially resolved. Here we show that adult rat hippocampal neural stem and progenitor cells (AH-NSPCs) express receptors for bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and that the BMP/P-Smad pathway is active in AH-NSPCs undergoing differentiation towards the neuronal lineage. In vitro, exposure to the BMP2 and BMP4 ligands is sufficient to increase neurogenesis from AH-NSPCs in a WNT dependent manner while decreasing oligodendrogenesis. Moreover, BMP2/4 and WNT3A, a key regulator of adult hippocampal neurogenesis, cooperate to further enhance neuronal production. Our data point to a mechanistic convergence of the BMP and WNT pathways at the level of the T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor gene Lef1. Altogether, we provide evidence that BMP signalling is an important regulator for the neuronal fate specification of AH-NSPCs cultures and we show that it significantly cooperates with the previously described master regulator of adult hippocampal neurogenesis, the WNT signalling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

