Mycobacterium terramassiliense, Mycobacterium rhizamassiliense and Mycobacterium numidiamassiliense sp. nov., three new Mycobacterium simiae complex species cultured from plant roots
- PMID: 29915369
- PMCID: PMC6006331
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-27629-1
Mycobacterium terramassiliense, Mycobacterium rhizamassiliense and Mycobacterium numidiamassiliense sp. nov., three new Mycobacterium simiae complex species cultured from plant roots
Abstract
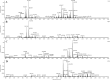
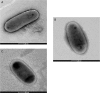
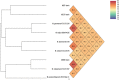
Three slowly growing mycobacteria named strain AB308, strain AB215 and strain AB57 were isolated from the tomato plant roots. The 16S rRNA and rpoB gene sequence analyses suggested that each strain was representative of one hitherto unidentified slowly-growing Mycobacterium species of the Mycobacterium simiae complex. Genome sequencing indicated that each strain contained one chromosome of 6.015-6.029 Mbp. A total of 1,197, 1,239 and 1,175 proteins were found to be associated with virulence and 107, 76 and 82 proteins were associated with toxin/antitoxin systems for strains AB308, AB215 and AB57, respectively. The three genomes encode for secondary metabolites, with 38, 33 and 46 genes found to be associated with polyketide synthases/non-ribosomal peptide synthases and nine, seven and ten genes encoding for bacteriocins, respectively. The genome of strain AB308 encodes for one questionable prophage and three incomplete prophages, while only incomplete prophages were predicted in AB215 and AB57 genomes. Genetic and genomic data indicate that strains AB308, AB215 and AB57 are each representative of a new Mycobacterium species that we respectively named Mycobacterium terramassiliense, Mycobacterium numidiamassiliense and Mycobacterium rhizamassiliense.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium ahvazicum sp. nov., the nineteenth species of the Mycobacterium simiae complex.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 7;8(1):4138. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22526-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29515197 Free PMC article.
-
"Mycobacterium massilipolynesiensis" sp. nov., a rapidly-growing mycobacterium of medical interest related to Mycobacterium phlei.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 11;7:40443. doi: 10.1038/srep40443. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28074866 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium talmoniae sp. nov., a slowly growing mycobacterium isolated from human respiratory samples.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017 Aug;67(8):2640-2645. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001998. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28809146
-
Mycobacterium lutetiense sp. nov., Mycobacterium montmartrense sp. nov. and Mycobacterium arcueilense sp. nov., members of a novel group of non-pigmented rapidly growing mycobacteria recovered from a water distribution system.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016 Sep;66(9):3694-3702. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001253. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27375118
-
Mycobacterium shinjukuense sp. nov., a slowly growing, non-chromogenic species isolated from human clinical specimens.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2011 Aug;61(Pt 8):1927-1932. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.025478-0. Epub 2010 Sep 10. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20833878
Cited by
-
Expanding the Bacterial Diversity of the Female Urinary Microbiome: Description of Eight New Corynebacterium Species.Microorganisms. 2023 Feb 3;11(2):388. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020388. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36838353 Free PMC article.
-
A New Perspective for Vineyard Terroir Identity: Looking for Microbial Indicator Species by Long Read Nanopore Sequencing.Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 6;11(3):672. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030672. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985245 Free PMC article.
-
Amycolatopsis camponoti sp. nov., new tetracenomycin-producing actinomycete isolated from carpenter ant Camponotus vagus.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2022 Apr;115(4):533-544. doi: 10.1007/s10482-022-01716-w. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2022. PMID: 35218449 Free PMC article.
-
Draft genome sequences of five Mycobacterium strains, isolated from Alnus glutinosa root nodules.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024 Feb 15;13(2):e0113223. doi: 10.1128/mra.01132-23. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024. PMID: 38189310 Free PMC article.
-
The soil microbiomics of intact, degraded and partially-restored semi-arid succulent thicket (Albany Subtropical Thicket).PeerJ. 2021 Oct 6;9:e12176. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12176. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34707927 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Egamberdiyeva D, Höflich G. Effect of plant growth-promoting bacteria on growth and nutrient uptake of cotton and pea in a semi-arid region of Uzbekistan. J. Arid Environ. 2004;56:293–301. doi: 10.1016/S0140-1963(03)00050-8. - DOI
-
- Egamberdieva D. Colonization of Mycobacterium phlei in the rhizosphere of wheat grown under saline conditions. Turkish J. Biol. 2012;36:487–492.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

