Cryo-EM structures of complex I from mouse heart mitochondria in two biochemically defined states
- PMID: 29915388
- PMCID: PMC6054875
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-018-0073-1
Cryo-EM structures of complex I from mouse heart mitochondria in two biochemically defined states
Abstract
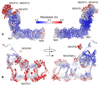
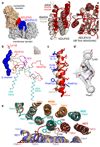
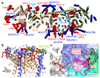
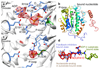
Complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) uses the reducing potential of NADH to drive protons across the energy-transducing inner membrane and power oxidative phosphorylation in mammalian mitochondria. Recent cryo-EM analyses have produced near-complete models of all 45 subunits in the bovine, ovine and porcine complexes and have identified two states relevant to complex I in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Here, we describe the 3.3-Å structure of complex I from mouse heart mitochondria, a biomedically relevant model system, in the 'active' state. We reveal a nucleotide bound in subunit NDUFA10, a nucleoside kinase homolog, and define mechanistically critical elements in the mammalian enzyme. By comparisons with a 3.9-Å structure of the 'deactive' state and with known bacterial structures, we identify differences in helical geometry in the membrane domain that occur upon activation or that alter the positions of catalytically important charged residues. Our results demonstrate the capability of cryo-EM analyses to challenge and develop mechanistic models for mammalian complex I.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

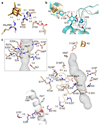
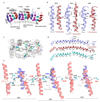
References
-
- Hirst J. Mitochondrial complex I. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:551–575. - PubMed
-
- Fassone E, Rahman S. Complex I deficiency: clinical features, biochemistry and molecular genetics. J Med Genet. 2012;49:578–590. - PubMed
-
- Hirst J, Carroll J, Fearnley IM, Shannon RJ, Walker JE. The nuclear encoded subunits of complex I from bovine heart mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1604:135–150. - PubMed
-
- Stroud DA, et al. Accessory subunits are integral for assembly and function of human mitochondrial complex I. Nature. 2016;538:123–126. - PubMed
-
- Sazanov LA, Hinchliffe P. Structure of the hydrophilic domain of respiratory complex I from Thermus thermophilus. Science. 2006;311:1430–1436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

