High-resolution cone beam CT for evaluation of vascular channel in intracranial partial thrombosed aneurysm
- PMID: 29915445
- PMCID: PMC5995734
- DOI: 10.18999/nagjms.80.2.279
High-resolution cone beam CT for evaluation of vascular channel in intracranial partial thrombosed aneurysm
Abstract
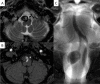
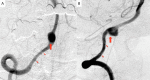
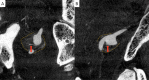
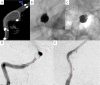
The authors present a 60-year-old man with a partially thrombosed, intracranial vertebral artery aneurysm. A vascular channel in intra-aneurysmal thrombus was effectively identified with high-resolution cone beam CT (DynaCT Micro: Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany). Pre-procedural vertebral angiogram implied a perforating artery arising from near neck of the aneurysm and DynaCT Micro performed before approaching to the lesion demonstrated a vascular channel running in intra-aneurysmal thrombus which could not be distinguished from perforators with other imaging modalities. It was confirmed that perforators around the aneurysm were not identified and safely treated the aneurysm with stent-assisted coil embolization. High-resolution cone beam CT is enable to sharply visualize vessel lumens, thrombus, and intra-thrombus structures, and is useful to identify a vascular channel in intracranial partially thrombosed aneurysm.
Keywords: angiogram; cone beam CT; intracranial aneurysm; thrombosed aneurysm; vascular channel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Intraaneurysmal embolization and parent artery trapping to treat a giant partial thrombosed vertebral artery aneurysm after surgical proximal clipping].No Shinkei Geka. 2000 Sep;28(9):817-22. No Shinkei Geka. 2000. PMID: 11025883 Japanese.
-
Efficacy of high-resolution cone-beam CT in the evaluation of perforators in vertebral artery dissection.Interv Neuroradiol. 2017 Aug;23(4):350-356. doi: 10.1177/1591019917706190. Epub 2017 May 16. Interv Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 28509611 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-aneurysmal hemodynamic alterations by a self-expandable intracranial stent and flow diversion stent: high intra-aneurysmal pressure remains regardless of flow velocity reduction.J Neurointerv Surg. 2013 Nov;5 Suppl 3:iii38-42. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2012-010488. Epub 2012 Oct 9. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013. PMID: 23048176
-
[Giant partially thrombosed aneurysm of the vertebral artery: a case report and literature review].Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2016;80(5):106-115. doi: 10.17116/neiro2016805106-115. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2016. PMID: 28635695 Review. Russian.
-
Multistage "Hybrid" (Open and Endovascular) Surgical Treatment of Vertebral Artery-Thrombosed Giant Aneurysm by Trapping and Thrombectomy.World Neurosurg. 2018 Jun;114:144-150. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.03.055. Epub 2018 Mar 16. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29551721 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of High-Resolution Flat Detector Computed Tomography in Stent Implantation for Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis.Front Neurosci. 2021 Aug 27;15:655594. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.655594. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34512235 Free PMC article.
-
Combined open revascularization and endovascular treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms: case series.Front Neurol. 2023 Apr 21;14:1102496. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1102496. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37153667 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS1 is upregulated in intracranial aneurysms and participates in the regulation of proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by upregulating TGF-β1.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Mar;17(3):1797-1801. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7144. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30867687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Endo H, Matsumoto Y, Kondo R, Sato K, Fujimura M, Inoue T, et al. Medullary infarction as a poor prognostic factor after internal coil trapping of a ruptured vertebral artery dissection. J Neurosurg, 2013; 118: 131–139. - PubMed
-
- Cho ZH, Kang CK, Han JY, Kim SH, Kim KN, Hong, SM, et al. Observation of the lenticulostriate arteries in the human brain in vivo using 7.0T MR angiography. Stroke, 2008; 39: 1604–1606. - PubMed
-
- Ding D, Starke RM, Durst CR, Gaughen JR Jr, Evans AJ, Jensen ME, et al. DynaCT imaging for intraprocedural evaluation of flow-diverting stent apposition during endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. J Clin Neurosci, 2014; 21: 1981–1983. - PubMed
-
- Tee JW, Dally M, Madan A, Hwang P. Surgical treatment of poorly visualised and complex cerebrovascular lesions using pre-operative angiographic data as angiographic DynaCT datasets for frameless stereotactic navigation. Acta Neurochir (Wien), 2012; 154: 1159–67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
