Robotic Pancreaticoduodenectomy: Technical Considerations
- PMID: 29915476
- PMCID: PMC5991022
- DOI: 10.1007/s12262-017-1628-9
Robotic Pancreaticoduodenectomy: Technical Considerations
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Robotic Pancreaticoduodenectomy: Technical Considerations.Indian J Surg. 2018 Aug;80(4):401. doi: 10.1007/s12262-018-1785-5. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Indian J Surg. 2018. PMID: 31525250 Free PMC article.
Abstract
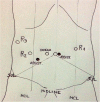
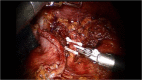
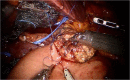
Robotic surgery can help to overcome some technical limitations of laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy thanks to EndoWrist instrumentations and the 3D view. Despite the potential benefits, its employment is still low and controversial. We focused on some important technical details crucial for a safe robotic pancreatectomy. After performing 52 robotic pancreatic resections that included 10 pancreatoduodenectomies, the authors describe their technique. The review of literature on robotic and laparoscopic duodenopancreatectomy is also performed in order to evaluate possible benefits of the robotic platform. We describe the step-by-step surgical procedure, analyzing all possible troubleshooting occurring in an initial center experience. The estimated blood loss as well as the length of stay was reduced by the robotic approach. We did not observe any significant increase of pancreatic fistula rate and all other postoperative complications despite our initial learning curve. Robotic pancreatoduodenectomy is a technically advanced procedure that requires important laparoscopic and robotic skills but it shows to be safe, feasible with some clear advantages in the bleeding control and in the reconstructive phase of the procedure.
Keywords: Learning curve; Operative technique; Pancreatic fistula; Robotic pancreatoduodenectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with Ethical StandardsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mehrabi A, Hafezi M, Arvin J, Esmaeliziadeh M, Garoussi C, Emami G, Kossler-Ebs J, Muller-Stich B, Buchler M, Hackert T, Diener MK. A systematic review and meta-analysis of laparoscopic versus open distal pancreatectomy for benign and malignant lesions of the pancreas: it’s time to randomize. Surgery. 2015;157(1):45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2014.06.081. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boggi U, Palladino S, Massimetti G, Vistoli F, Caniglia F, De Lio N, Perrone V, Barbarello L, Belluomini M, Signori S, Amorese G, Mosca F. Laparoscopic robot-assisted versus open total pancreatectomy: a case-matched study. Surg Endosc. 2015;29(6):1425–1432. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3819-9. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources