A retrospective study of bovine tuberculosis at the municipal abattoir of Bauchi State, Northeastern Nigeria
- PMID: 29915497
- PMCID: PMC5993755
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2018.598-605
A retrospective study of bovine tuberculosis at the municipal abattoir of Bauchi State, Northeastern Nigeria
Abstract
Background and aim: Bovine tuberculosis (bTB) still remains a major zoonotic bacterial disease affecting livestock and humans worldwide. The disease remains a poorly managed tropical disease in most developing countries of the world; where in addition to productivity losses and significance in international trade, it posed a major public health threat to both humans and animals. A retrospective study was designed to investigate the occurrence of bTB lesions at Bauchi municipal abattoir.
Materials and methods: The study utilized abattoir records spanning a period of 10 years (2004-2013). The records indicated that a total of 1,08,638 heads of cattle comprising n = 56,070 males and n = 52,570 females were slaughtered at the municipal abattoir during the study period.
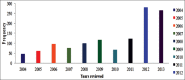
Result: Of these heads, n = 1230 (1.13%) (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.07, 1.19) had tuberculous lesions. The annual occurrence during the study period varied significantly (p<0.001) from 0.53% (95% CI: 0.40, 0.67) to 1.87% (95% CI: 1.66, 2.10) in 2010 and 2012, respectively. Females had a significantly higher (p<0.001) prevalence of 2.10% (95% CI: 1.98, 2.23) compared with the males 0.23% (95% CI: 0.19, 0.27). The distribution of suspected gross bTB lesions in different organs showed 11.87% in the lungs, 5.93% in the liver, 1.14% in the heart, and 0.49% accounted for generalized bTB. However, none was observed on the lymph nodes and intestines.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that bTB persists in Bauchi State with annual variations during the study period. This study highlights the importance of meat inspection as an important tool for detecting the presence of bTB lesions.
Keywords: Bauchi; Mycobacterium bovis; bovine tuberculosis; prevalence; retrospective.
Figures

References
-
- Biu A. Chorioptic mange infestation in cattle in Borno State, Nigeria. Pak. Vet. J. 2004;24:155–156.
-
- OIE. OIE-Listed Diseases, Infections and Infestation in Force in 2018. 2018. [Accessed on 26-03-2018]. http://www.oie.int/animal-health-in-the-world/oie-listed-diseases-2018/
-
- Regassa A, Medhin G, Ameni G. Bovine tuberculosis is more prevalent in cattle owned by farmers with active tuberculosis in central Ethiopia. Vet. J. 2008;178:119–125. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
