Performance Comparison of Different Readouts for Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Arrays
- PMID: 29915669
- PMCID: PMC6003720
- DOI: 10.1088/2057-1976/aa7c6a
Performance Comparison of Different Readouts for Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Arrays
Abstract
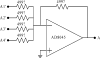
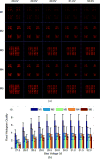
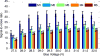
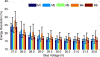
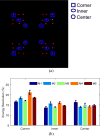
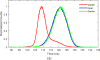
A thorough comparison of five different readouts for reading out a 2 × 2 array of 5 mm × 5 mm position-sensitive solid-state photomultipliers (PS-SSPM) was undertaken. The five readouts include reading out the 20 signals (16 position and 4 timing) individually, two signal multiplexing readouts, and two position decoding readouts. Flood histogram quality, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and energy resolution were compared at different bias voltage (27.0 V to 32.0 V, at 0.5 V intervals) and at a fixed temperature of 0 °C by coupling a 6 × 6 array of 1.3 mm × 1.3 mm × 20 mm polished LSO crystals to the center of the PS-SSPM array. The timing resolution was measured at a bias voltage of 31.0 V (optimal bias voltage in terms of flood histogram quality). The best flood histogram quality value and signal-to-noise were 7.3 ± 1.6 and 33.5 ± 3.1, respectively, and were obtained by shaping and digitizing the 16 position signals individually. The capacitive charge-division readout is the simplest readout among the five evaluated but still resulted in good performance with a flood histogram quality value of 3.3 ± 0.4 and a SNR of 18.3 ± 1.3. The average energy resolution and the average timing resolution were 15.2 ± 1.2 % and 8.4 ± 1.6 ns for individual signal readout and 15.9 ± 1.2 % and 8.8 ± 1.3 ns by using the capacitive charge-division readout method. These studies show that for an ultra-high spatial resolution applications using the 2 × 2 PS-SSPM array, reading out the 20 signals individually is necessary; whilst the capacitive charge-division readout is a cost-effective readout for less demanding applications.
Keywords: PET; charge division readout; position-sensitive solid-state photomultipliers.
Figures



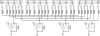



Similar articles
-
A Simple Capacitive Charge-Division Readout for Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Arrays.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2013 Oct;60(5):3188-3197. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2013.2275012. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2013. PMID: 25558081 Free PMC article.
-
Performance comparison of two signal multiplexing readouts for SiPM-based pet detector.Phys Med Biol. 2019 Dec 5;64(23):23NT02. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab5738. Phys Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31722318
-
Comparison of large-area position-sensitive solid-state photomultipliers for small animal PET.Phys Med Biol. 2012 Dec 21;57(24):8119-34. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/24/8119. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Phys Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23172720
-
A Study of Position-Sensitive Solid-State Photomultiplier Signal Properties.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2014 Jun 12;61(3):1074-1083. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2014.2302635. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2014. PMID: 25473125 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Matrix9 silicon photomultiplier array for small-animal PET.Med Phys. 2015 Feb;42(2):585. doi: 10.1118/1.4905088. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 25652479 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PET Detectors Based on Multi-Resolution SiPM Arrays.IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2024 May;8(5):493-500. doi: 10.1109/trpms.2024.3381865. Epub 2024 Mar 26. IEEE Trans Radiat Plasma Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39553417 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
