Low-level laser treatment applied at auriculotherapy points to reduce postoperative pain in third molar surgery: A randomized, controlled, single-blinded study
- PMID: 29920521
- PMCID: PMC6007895
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197989
Low-level laser treatment applied at auriculotherapy points to reduce postoperative pain in third molar surgery: A randomized, controlled, single-blinded study
Abstract
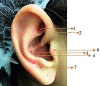
Objective: Evaluate the effectiveness of LLL (Low level laser therapy) in auriculotherapy points for pain reduction following lower third molar extractions.
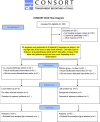
Study design: Randomized, controlled, single-blinded study.
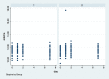
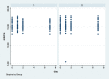
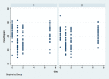
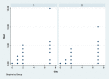
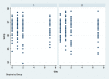
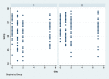
Methods: Eighty-four bilateral, symmetrical third molar surgeries were performed in 42 healthy patients using a split-mouth design. In the immediate postoperative period, each side was randomly treated in a single-blind method with an LLL at the auriculotherapy points or simulation of its use (contralateral side) over a 21-day interval. This protocol was repeated 24 and 48 hours after surgery. All patients used the same analgesic (paracetamol) but only in case of pain. The primary variable was postoperative pain according to the visual analogue scale, and the secondary variables were mouth opening, edema, local temperature, dysphagia, and the presence of infection (systemic temperature, lymphadenopathy). These variables were evaluated at baseline and at 24 hours, 48 hours and seven days after surgery. Adverse effects were recorded and reported.
Results: There was no difference between the groups in relation to any of the evaluated parameters (p>0.05).
Conclusion: For this experimental model, application of a low-intensity laser at auriculotherapy points did not prevent postoperative pain following lower third molar surgery.
Trial registration: This trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov; the registration number is NCT02657174 and the Unique Protocol ID number is 1.100.869. (https://register.clinicaltrials.gov/prs/app/template/EditRecord.vm?epmode=View&listmode=Edit&uid=U0002BEY&ts=11&sid=S0006026&cx=6g4wff).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Pouchain EC, Costa FWG. Bezerra TP, Soares ECS. Comparative efficacy of nimesulide and ketoprofen on inflammatory events in third molar surgery: a Split-mouth, prospective, randomized, double-bilnd study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44:876–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2014.10.026 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ferrante M, Petrini M,Trentini P, Perfetti G, Spoto G. Effect of low-level therapy after extraction of impacted lower third molars. Lasers Med Sci. 2013; 28:845–849. doi: 10.1007/s10103-012-1174-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Markovic AB, Todorovic L, Postoperative analgesia after lower third molar surgery: contribution of the use of long-acting local anesthetics, low-power laser, and diclofenac. Oral Surg, Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102:e4–8. - PubMed
-
- Ustün Y, Erdogan O, Esen E, Karsli ED. Comparison of the effects of 2 doses of methylprednisolone on pain, swelling, and trismus after third molar surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003;96:535–9. doi: 10.1016/S1079210403004645 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zuniga J R, Phillips C L,Shugars D, Lyon J A, Peroutika S J, Swarbric J et al. Analgesic safety and efficacy of diclofenac sodium softgels on postoperative third molar extraction pain–J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62: 806–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

