Effects of intramuscular morphine in men and women with temporomandibular disorder with myofascial pain
- PMID: 29920852
- PMCID: PMC6193838
- DOI: 10.1111/odi.12919
Effects of intramuscular morphine in men and women with temporomandibular disorder with myofascial pain
Abstract
Objectives: This placebo-controlled randomized double-blinded clinical study assessed the analgesic efficacy of intramuscular morphine in TMD patients with myofascial pain and sex-dependent responses of the morphine treatment.
Subjects and methods: Men and women with TMD were treated with morphine (1.5 or 5 mg), lidocaine, or saline in the masseter muscle. VAS of pain intensity, PPT, and PPtol were compared between treatment groups and gender. An additional group was treated with morphine in the trapezius muscle to evaluate the systemic effect of morphine that may reduce pain in the masseter muscle.
Results: There was a significant difference in VAS scores between the morphine 5 mg group and the saline group favoring morphine, but not between the morphine 5 mg and lidocaine. Morphine 1.5 and 5 mg treatments led to consistently and significantly elevated PPT and PPtol measures in men, but not in women. Morphine administered in the trapezius muscle did not affect the outcome measures.
Conclusion: A single dose intramuscular morphine produced analgesic effects up to 48 hr in patients with myofascial pain. Intramuscular morphine elevated mechanical pain threshold and tolerance in the masseter only in male patients, suggesting sex differences in local morphine effects. No systemic effect of intramuscular morphine was detected.
Keywords: masseter; muscle pain; opioid receptor; peripheral; trigeminal.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
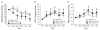


Similar articles
-
Increased pain and muscle glutamate concentration after single ingestion of monosodium glutamate by myofascial temporomandibular disorders patients.Eur J Pain. 2016 Oct;20(9):1502-12. doi: 10.1002/ejp.874. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Eur J Pain. 2016. PMID: 27091318 Clinical Trial.
-
Analgesic effects of intra-articular morphine in patients with temporomandibular joint disorders: a prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010 Mar;68(3):622-7. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2009.04.049. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20171481 Clinical Trial.
-
Nerve growth factor-evoked masseter muscle sensitization and perturbation of jaw motor function in healthy women.J Orofac Pain. 2008 Fall;22(4):340-8. J Orofac Pain. 2008. PMID: 19090407 Clinical Trial.
-
Glutamate-evoked jaw muscle pain as a model of persistent myofascial TMD pain?Arch Oral Biol. 2008 Jul;53(7):666-76. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2008.01.008. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Arch Oral Biol. 2008. PMID: 18313028 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nociception and the neonatal brain.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019 Aug;24(4):101016. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2019.05.008. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019. PMID: 31201139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Treatments of Temporomandibular Disorders: A Systematic Review Including a Network Meta-Analysis.Drugs. 2024 Jan;84(1):59-81. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01971-9. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38103150 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends Related to the Publication of Clinical Trials on the Treatment of Temporomandibular Disorders Between 1973 and 2023.Int J Dent. 2025 Aug 6;2025:8594730. doi: 10.1155/ijod/8594730. eCollection 2025. Int J Dent. 2025. PMID: 40808853 Free PMC article.
-
Peripherally Acting Opioids in Orofacial Pain.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 4;15:665445. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.665445. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34017236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intramuscular Injections and Dry Needling within Masticatory Muscles in Management of Myofascial Pain. Systematic Review of Clinical Trials.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Sep 10;18(18):9552. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189552. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34574476 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical models of deep craniofacial nociception and temporomandibular disorder pain.Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021 Nov;57:231-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2021. PMID: 34815817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Binning AR, Przesmycki K, Sowinski P, Morrison LM, Smith TW, Marcus P, Lees JP, Dahan A. A randomised controlled trial on the efficacy and side-effect profile (nausea/vomiting/sedation) of morphine-6-glucuronide versus morphine for post-operative pain relief after major abdominal surgery. European journal of pain. 2011;15:402–8. - PubMed
-
- Cai BB, Cairns BE, Sessle BJ, Hu JW. Sex-related suppression of reflex jaw muscle activity by peripheral morphine but not GABA. Neuroreport. 2001;12:3457–60. - PubMed
-
- Coggeshall RE, Zhou S, Carlton SM. Opioid receptors on peripheral sensory axons. Brain research. 1997;764:126–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

