Loading of malonyl-CoA onto tandem acyl carrier protein domains of polyunsaturated fatty acid synthases
- PMID: 29921583
- PMCID: PMC6093242
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002443
Loading of malonyl-CoA onto tandem acyl carrier protein domains of polyunsaturated fatty acid synthases
Abstract
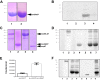
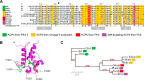
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are produced in some unicellular organisms, such as marine gammaproteobacteria, myxobacteria, and thraustochytrids, by large enzyme complexes called PUFA synthases. These enzymatic complexes resemble bacterial antibiotic-producing proteins known as polyketide synthases (PKS). One of the PUFA synthase subunits is a conserved large protein (PfaA in marine proteobacteria) that contains three to nine tandem acyl carrier protein (ACP) domains as well as condensation and modification domains. In this work, a study of the PfaA architecture and its ability to initiate the synthesis by selecting malonyl units has been carried out. As a result, we have observed a self-acylation ability in tandem ACPs whose biochemical mechanism differ from the previously described for type II PKS. The acyltransferase domain of PfaA showed a high selectivity for malonyl-CoA that efficiently loads onto the ACPs domains. These results, together with the structural organization predicted for PfaA, suggest that this protein plays a key role at early stages of the anaerobic pathway of PUFA synthesis.
Keywords: acyl carrier protein (ACP); acyltransferase; fatty acid synthase (FAS); polyketide; polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).
© 2018 Santín and Moncalián.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




References
-
- Gemperlein K., Rachid S., Garcia R. O., Wenzel S. C., and Müller R. (2014) Polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis in myxobacteria: different PUFA synthases and their product diversity. Chem. Sci. 5, 1733–1741 10.1039/c3sc53163e - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

