The Type 3 Deiodinase: Epigenetic Control of Brain Thyroid Hormone Action and Neurological Function
- PMID: 29921775
- PMCID: PMC6032375
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19061804
The Type 3 Deiodinase: Epigenetic Control of Brain Thyroid Hormone Action and Neurological Function
Abstract
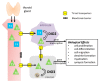
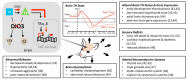
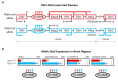
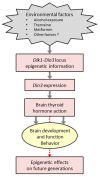
Thyroid hormones (THs) influence multiple processes in the developing and adult central nervous system, and their local availability needs to be maintained at levels that are tailored to the requirements of their biological targets. The local complement of TH transporters, deiodinase enzymes, and receptors is critical to ensure specific levels of TH action in neural cells. The type 3 iodothyronine deiodinase (DIO3) inactivates THs and is highly present in the developing and adult brain, where it limits their availability and action. DIO3 deficiency in mice results in a host of neurodevelopmental and behavioral abnormalities, demonstrating the deleterious effects of TH excess, and revealing the critical role of DIO3 in the regulation of TH action in the brain. The fact the Dio3 is an imprinted gene and that its allelic expression pattern varies across brain regions and during development introduces an additional level of control to deliver specific levels of hormone action in the central nervous system (CNS). The sensitive epigenetic nature of the mechanisms controlling the genomic imprinting of Dio3 renders brain TH action particularly susceptible to disruption due to exogenous treatments and environmental exposures, with potential implications for the etiology of human neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: Dio3; Dlk1-Dio3 genomic imprinting; behavior; brain development; brain morphology; environmental factors; neuroendocrine function; sensory function; thyroid hormone; type 3 deiodinase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genomic imprinting of the type 3 thyroid hormone deiodinase gene: regulation and developmental implications.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jul;1830(7):3946-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.03.015. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22498139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenerational epigenetic self-memory of Dio3 dosage is associated with Meg3 methylation and altered growth trajectories and neonatal hormones.Epigenetics. 2024 Dec;19(1):2376948. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2024.2376948. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38991122 Free PMC article.
-
Type 3 Deiodinase Role on Central Thyroid Hormone Action Affects the Leptin-Melanocortin System and Circadian Activity.Endocrinology. 2017 Feb 1;158(2):419-430. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1680. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 27911598 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic imprinting variations in the mouse type 3 deiodinase gene between tissues and brain regions.Mol Endocrinol. 2014 Nov;28(11):1875-86. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1210. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Mol Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 25232934 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuning notes in the behavioral symphony: parent-of-origin allelic gene expression in the brain.Adv Genet. 2014;86:93-106. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800222-3.00005-X. Adv Genet. 2014. PMID: 25172347 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Autoimmunity to the Thyroid Hormone Monocarboxylate Transporters MCT8 and MCT10.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 30;9(5):496. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050496. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33946552 Free PMC article.
-
Deiodinase Types 1 and 3 and Proinflammatory Cytokine Values May Discriminate Depressive Disorder Patients from Healthy Controls.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 24;12(19):6163. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196163. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834806 Free PMC article.
-
Iodine Deficiency, Maternal Hypothyroxinemia and Endocrine Disrupters Affecting Fetal Brain Development: A Scoping Review.Nutrients. 2023 May 9;15(10):2249. doi: 10.3390/nu15102249. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242131 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics of Neurodevelopmental Disorders Comes of Age with Roles in Clinical and Educational Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 12;19(9):2720. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092720. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30213026 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-level hypothalamic neuromodulation of self-regulation and cognition in preterm infants: Towards a control systems model.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2021 Dec 31;9:100109. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2021.100109. eCollection 2022 Feb. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2021. PMID: 35755927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Legrand J. Effects of thyroid hormones on central nervous system development. In: Yanai J., editor. Neurobehavioral Teratology. Elsevier; New York, NY, USA: 1984. pp. 331–363.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

