Isoflavones enhance pharmacokinetic exposure of active lovastatin acid via the upregulation of carboxylesterase in high-fat diet mice after oral administration of Xuezhikang capsules
- PMID: 29921884
- PMCID: PMC6289385
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-018-0039-1
Isoflavones enhance pharmacokinetic exposure of active lovastatin acid via the upregulation of carboxylesterase in high-fat diet mice after oral administration of Xuezhikang capsules
Abstract
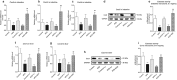
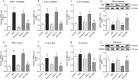
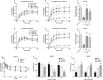
Xuezhikang capsule (XZK) is a traditional Chinese medicine that contains lovastatin (Lv) for hyperlipidemia treatment, although it has fewer side effects than Lv. However, the pharmacokinetic mechanisms contributing to its distinct efficacy and low side effects are unclear. Mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 6 weeks to induce hyperlipidemia. We first conducted the pharmacokinetic studies in HFD mice following oral administration of Lv (10 mg/kg, i.g.) and found that HFD remarkably decreased the active form of Lv (the lovastatin acid, LvA) exposure in the circulation system, especially in the targeting organ liver, with a declined conversion from Lv to LvA, whereas the Lv (responsible for myotoxicity) exposure in muscle markedly increased. Then we compared the pharmacokinetic profiles of Lv in HFD mice after the oral administration of XZK (1200 mg/kg, i.g.) or an equivalent dose of Lv (10 mg/kg, i.g.). A higher exposure of LvA and lower exposure of Lv were observed after XZK administration, suggesting a pharmacokinetic interaction of some ingredients in XZK. Further studies revealed that HFD promoted the inflammation and inhibited carboxylesterase (CES) activities in the intestine and the liver, thus contributing to the lower transformation of Lv into LvA. In contrast, XZK inhibited the inflammation and upregulated CES in the intestine and the liver. Finally, we evaluated the effects of monacolins and phytosterols, the fractional extracts of isoflavones, on inflammatory LS174T or HepG2 cells, which showed that isoflavones inhibited inflammation, upregulated CES, and markedly enhanced the conversion of Lv into LvA. For the first time, we provide evidence that isoflavones and Lv in XZK act in concert to enhance the efficacy and reduce the side effects of Lv.
Keywords: Xuezhikang capsules; carboxylesterase; hyperlipidemia; inflammation; isoflavones; lovastatin; lovastatin acid; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Isoflavones and phytosterols contained in Xuezhikang capsules modulate cholesterol homeostasis in high-fat diet mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Dec;36(12):1462-72. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.98. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 26592515 Free PMC article.
-
Xuezhikang improves the outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats by suppressing the inflammation response through TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jun;114:108817. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108817. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30953818
-
The effect of Xuezhikang capsule on gene expression profile in brown adipose tissue of obese spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Feb 10;302(Pt A):115700. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115700. Epub 2022 Sep 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36126782
-
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Similarities and differences.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 May;32(5):403-25. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199732050-00005. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997. PMID: 9160173 Review.
-
Lovastatin. A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic properties and therapeutic use in hyperlipidaemia.Drugs. 1988 Oct;36(4):429-54. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198836040-00003. Drugs. 1988. PMID: 3069436 Review.
Cited by
-
Association analysis of gut microbiota-metabolites-neuroendocrine changes in male rats acute exposure to simulated altitude of 5500 m.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 7;13(1):9225. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35573-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37286697 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of an orally active VHL-recruiting PROTAC that achieves robust HMGCR degradation and potent hypolipidemic activity in vivo.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 May;11(5):1300-1314. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.11.001. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34094835 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic, updated review of Xuezhikang, a domestically developed lipid-lowering drug, in the application of cardiovascular diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Oct;14(10):4228-4242. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.011. Epub 2024 May 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39525586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statins and Hemostasis: Therapeutic Potential Based on Clinical Evidence.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1408:25-47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-26163-3_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37093420 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Active Ingredients of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Carthamus tinctorius in Compatibility in Normal and Cerebral Ischemia Rats: A Comparative Study.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020 Apr;45(2):273-284. doi: 10.1007/s13318-019-00597-1. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 31828667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen ZY, Ma KY, Liang Y, Peng C, Zuo Y. Role and classification of cholesterol-lowering functional foods. J Funct Foods. 2011;3:61–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2011.02.003. - DOI
-
- Gropper SS, Smith LJ, Groff LJ. Advanced nutrition and human metabolism. 7th ed. Ohio (USA): Peter Marshall, Wadsworth; 2005.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

