Late-life targeting of the IGF-1 receptor improves healthspan and lifespan in female mice
- PMID: 29921922
- PMCID: PMC6008442
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04805-5
Late-life targeting of the IGF-1 receptor improves healthspan and lifespan in female mice
Abstract
Diminished growth factor signaling improves longevity in laboratory models, while a reduction in the somatotropic axis is favorably linked to human aging and longevity. Given the conserved role of this pathway on lifespan, therapeutic strategies, such as insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) monoclonal antibodies (mAb), represent a promising translational tool to target human aging. To this end, we performed a preclinical study in 18-mo-old male and female mice treated with vehicle or an IGF-1R mAb (L2-Cmu, Amgen Inc), and determined effects on aging outcomes. Here we show that L2-Cmu preferentially improves female healthspan and increases median lifespan by 9% (P = 0.03) in females, along with a reduction in neoplasms and inflammation (P ≤ 0.05). Thus, consistent with other models, targeting IGF-1R signaling appears to be most beneficial to females. Importantly, these effects could be achieved at advanced ages, suggesting that IGF-1R mAbs could represent a promising therapeutic candidate to delay aging.
Conflict of interest statement
P.J.B. and H.S.-M. are currently or previously employed by Amgen, Inc. All the remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
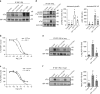


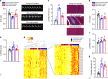


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 ES020812/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG037574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM090311/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG021654/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG052981/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG023475/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG034906/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013319/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG018381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG055369/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG050886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG038072/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK026687/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

