Blood-Derived microRNAs for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: A Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 29922178
- PMCID: PMC5996199
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00685
Blood-Derived microRNAs for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: A Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
microRNAs (miRNAs) have been reported to be aberrantly expressed in patients with pancreatic cancer. In present review we explored the biological roles of miRNAs in pancreatic cancer and their clinical value in diagnosis. In the systematic review, the potential value of miRNAs as biomarkers was investigated by reviewing the altered miRNA profiles reported in pancreatic cancer patients in 356 included studies. In the subsequent meta-analysis, we included 17 studies in early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer with a panel of altered miRNAs. The following results were obtained: pooled sensitivity of 0.88 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.83-0.92), pooled specificity of 0.83 (95%CI 0.77-0.88), diagnostic odds ratio of 27 (95%CI 14-53), and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.90 (95%CI 0.88-0.93). To further explore the value of a single miRNA, the diagnostic value of miR-21 in PA was also demonstrated by the pooled sensitivity (0.90, 95% CI: 0.82-0.94), specificity (0.72, 95% CI: 0.57-0.83) as well as AUC (0.91 (95%CI 0.88-0.93). In conclusion, our findings suggest that aberrant miRNA expression in blood play an essential role in pancreatic cancer, and meta-analysis revealed blood-derived miRNAs as probable biomarkers for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: blood; diagnosis; differential; meta-analysis; microRNAs; pancreatic cancer.
Figures


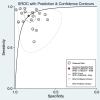
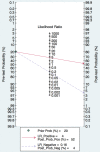
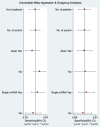

Comment in
-
Commentary: Blood-Derived microRNAs for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis: A Narrative Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 22;9:1896. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01896. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30723420 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bhatti I., James V., Hall R. I., Lund J. N., Tufarelli C., Lobo D. N., et al. (2011). Knockdown of microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation and increases cell death by targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Soc. Surg. Aliment. Tract. 15, 199–208. 10.1007/s11605-010-1381-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cote G. A., Gore A. J., McElyea S. D., Heathers L. E., Xu H., Sherman S., et al. (2014). A pilot study to develop a diagnostic test for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on differential expression of select miRNA in plasma and bile. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 109, 1942. 10.1038/ajg.2014.331 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

