Immunolocalization and Changes of Hydroxyproline-Rich Glycoproteins During Symbiotic Germination of Dendrobium officinale
- PMID: 29922306
- PMCID: PMC5996918
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00552
Immunolocalization and Changes of Hydroxyproline-Rich Glycoproteins During Symbiotic Germination of Dendrobium officinale
Abstract
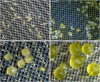
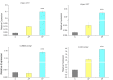
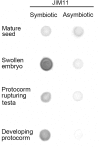
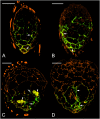
Hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) are abundant cell wall components involved in mycorrhizal symbiosis, but little is known about their function in orchid mycorrhizal association. To gain further insight into the role of HRGPs in orchid symbiosis, the location and function of HRGPs were investigated during symbiotic germination of Dendrobium officinale. The presence of JIM11 epitope in developing protocorms was determined using immunodot blots and immunohistochemical staining procedures. Real-time PCR was also employed to verify the expression patterns of genes coding for extensin-like genes selected from the transcriptomic database. The importance of HRGPs in symbiotic germination was further investigated using 3,4-dehydro-L-proline (3,4-DHP), an inhibitor of HRGP biosynthesis. In symbiotic cultures, immunodot blots of JIM11 signals were moderate in mature seeds, and the signals became stronger in swollen embryos. After germination, signal intensities decreased in developing protocorms. In contrast, in asymbiotic cultures, JIM11 signals were much lower as compared with those stages in symbiotic cultures. Immunofluorescence staining enabled the visualization of JIM11 epitope in mature embryo and protocorm cells. Positive signals were initially localized in the larger cells near the basal (suspensor) end of uninfected embryos, marking the future colonization site of fungal hyphae. After 1 week of inoculation, the basal end of embryos had been colonized, and a strong signal was detected mostly at the mid- and basal regions of the enlarging protocorm. As protocorm development progressed, the signal was concentrated in the colonized cells at the basal end. In colonized cells, signals were present in the walls and intracellularly associated with hyphae and the pelotons. The precise localization of JIM11 epitope is further examined by immunogold labeling. In the colonized cells, gold particles were found mainly in the cell wall and the interfacial matrix near the fungal cell wall. Four extensin-like genes were verified to be highly up-regulated in symbiotically germinated protocorms as compared to asymbiotically germinated ones. The 3,4-DHP treatment inhibited the accumulation of HRGPs and symbiotic seed germination. In these protocorms, fungal hyphae could be found throughout the protocorms. Our results indicate that HRGPs play an important role in symbiotic germination. They can serve as markers for fungal colonization, establishing a symbiotic compartment and constraining fungal colonization inside the basal cells of protocorms.
Keywords: Dendrobium; hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins; immunolocalization; mycorrhiza; symbiotic germination.
Figures



Similar articles
-
What role does the seed coat play during symbiotic seed germination in orchids: an experimental approach with Dendrobium officinale.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jul 29;22(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03760-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35906552 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental localization and the role of hydroxyproline rich glycoproteins during somatic embryogenesis of banana (Musa spp. AAA).BMC Plant Biol. 2011 Feb 24;11:38. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-38. BMC Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21349190 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Insights into the Roles of Hormones in the Dendrobium officinale-Tulasnella sp. Germinated Seed Symbiotic Association.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 6;19(11):3484. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113484. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404159 Free PMC article.
-
A perspective on orchid seed and protocorm development.Bot Stud. 2017 Dec;58(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40529-017-0188-4. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Bot Stud. 2017. PMID: 28779349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orchid Reintroduction Based on Seed Germination-Promoting Mycorrhizal Fungi Derived From Protocorms or Seedlings.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jun 30;12:701152. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.701152. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34276753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ultrastructural changes during the symbiotic seed germination of Gastrodia elata with fungi, with emphasis on the fungal colonization region.Bot Stud. 2020 Feb 12;61(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40529-019-0280-z. Bot Stud. 2020. PMID: 32052210 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of different mycobionts on symbiotic germination and seedling growth of Dendrobium officinale, an important medicinal orchid.Bot Stud. 2020 Jan 27;61(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40529-019-0278-6. Bot Stud. 2020. PMID: 31989371 Free PMC article.
-
3,4-Dehydro-L-proline Induces Programmed Cell Death in the Roots of Brachypodium distachyon.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 14;22(14):7548. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147548. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299166 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Seed Germination of Cremastra appendiculata: Screening and Identification of Four New Symbiotic Fungi in the Psathyrellaceae Family.J Microbiol. 2024 Aug;62(8):671-682. doi: 10.1007/s12275-024-00148-7. Epub 2024 Jun 28. J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38940992
-
Role of Protein Glycosylation in Host-Pathogen Interaction.Cells. 2020 Apr 20;9(4):1022. doi: 10.3390/cells9041022. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32326128 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arditti J., Krikorian D. (1996). Orchid micropropagation: the path from laboratory to commercialization and an account of several unappreciated investigators. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 122 183–241. 10.1111/j.1095-8339.1996.tb02073.x - DOI
-
- Balestrini R., Bonfante P. (2005). The interface compartment in arbuscular mycorrhizae: a special type of plant cell wall? Plant Biosyst. 139 8–15. 10.1080/11263500500056799 - DOI
-
- Balestrini R., Jose-Estanyol M., Puigdomenech P., Bonfante P. (1997). Hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein mRNA accumulation in maize root cells colonized by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus as revealed by in situ hybridization. Protoplasma 198 36–42. 10.1007/bf01282129 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

