Identification and Characterization of Neuropeptides by Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses in a Bivalve Mollusc Patinopecten yessoensis
- PMID: 29922332
- PMCID: PMC5996578
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00197
Identification and Characterization of Neuropeptides by Transcriptome and Proteome Analyses in a Bivalve Mollusc Patinopecten yessoensis
Abstract
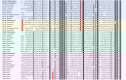
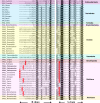
Neuropeptides play essential roles in regulation of reproduction and growth in marine molluscs. But their function in marine bivalves - a group of animals of commercial importance - is largely unexplored due to the lack of systematic identification of these molecules. In this study, we sequenced and analyzed the transcriptome of nerve ganglia of Yesso scallop Patinopecten yessoensis, from which 63 neuropeptide genes were identified based on BLAST and de novo prediction approaches, and 31 were confirmed by proteomic analysis using the liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Fifty genes encode known neuropeptide precursors, of which 20 commonly exist in bilaterians and 30 are protostome specific. Three neuropeptides that have not yet been reported in bivalves were identified, including calcitonin/DH31, lymnokinin and pleurin. Characterization of glycoprotein hormones, insulin-like peptides, allatostatins, RFamides, and some reproduction, cardioactivity or feeding related neuropeptides reveals scallop neuropeptides have conserved molluscan neuropeptide domains, but some (e.g., GPB5, APGWamide and ELH) are characterized with bivalve-specific features. Thirteen potentially novel neuropeptides were identified, including 10 that may also exist in other protostomes, and 3 (GNamide, LRYamide, and Vamide) that may be scallop specific. In addition, we found neuropeptides potentially related to scallop shell growth and eye functioning. This study represents the first comprehensive identification of neuropeptides in scallop, and would contribute to a complete understanding on the roles of various neuropeptides in endocrine regulation in bivalve molluscs.
Keywords: bivalve mollusc; cardioactivity; eye functioning; ganglia transcriptome; mass spectrometry; neuropeptide; reproduction; shell growth.
Figures




References
-
- Abdraba A. M., Saleuddin A. S. (2000). Protein synthesis in vitro by mantle tissue of the land snail Otala lactea: possible insulin-like peptide function. Can. J. Zool. 78 1527–1535. 10.1139/z00-030 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

