Association of vitamin D receptor BsmI, TaqI, FokI, and ApaI polymorphisms with susceptibility of chronic periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 38 case -control studies
- PMID: 29922333
- PMCID: PMC5958531
Association of vitamin D receptor BsmI, TaqI, FokI, and ApaI polymorphisms with susceptibility of chronic periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on 38 case -control studies
Abstract
Background: There has been increasing interest in the study of the association between Vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms and risk of chronic periodontitis. However, the results remain inconclusive. To better understand the roles of VDR polymorphisms (BsmI, TaqI, FokI, and ApaI) in chronic periodontitis susceptibility, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis.
Materials and methods: The PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science database were systemically searched to determine all the eligible studies about VDR polymorphisms and risk of chronic periodontitis up to April 2017. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to evaluate the associations between VDR polymorphisms and chronic periodontitis risk. All the statistical analyses were performed by Comprehensive Meta-Analysis. All P values were two-tailed with a significant level at 0.05.
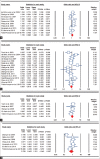
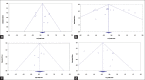
Results: Finally, a total of 38 case-control studies in 19 publications were identified which met our inclusion criteria. There are ten studies with 866 chronic periodontitis cases and 786 controls for BsmI, 16 studies with 1570 chronic periodontitis cases and 1676 controls for TaqI, five studies with 374 chronic periodontitis cases and 382 controls for FokI, and seven studies with 632 chronic periodontitis cases and 604 controls for ApaI. Overall, no significant association was observed between VDR gene BsmI, TaqI, FokI, and ApaI polymorphisms and risk of chronic periodontitis in any genetic model. Subgroup analysis stratified by ethnicity suggested a significant association between BsmI polymorphism and chronic periodontitis risk in the Caucasian subgroup under allele model (A vs. G: OR = 1.747, 95% CI = 1.099-2.778, P = 0.018). Further, no significant associations were observed when stratified by Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium status for BsmI, TaqI, and ApaI.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that BsmI, TaqI, FokI, and ApaI polymorphisms in the VDR gene might not be associated with risk of chronic periodontitis in overall population.
Keywords: Chronic periodontitis; Vitamin D receptor; meta-analysis; polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or nonfinancial in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms on the risk of chronic and aggressive periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the Chinese population.Arch Oral Biol. 2022 Dec;144:105566. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2022.105566. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Arch Oral Biol. 2022. PMID: 36279828
-
Associations among four polymorphisms (BsmI, FokI, TaqI and ApaI) of vitamin D receptor gene and end-stage renal disease: a meta-analysis.Arch Med Res. 2015 Jan;46(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2014.11.017. Epub 2014 Nov 27. Arch Med Res. 2015. PMID: 25434518 Review.
-
A meta-analysis of the association of ApaI, BsmI, FokI, and TaqI polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor gene with the risk of polycystic ovary syndrome in the Eastern Mediterranean Regional Office population.Int J Reprod Biomed. 2022 Jul 6;20(6):433-446. doi: 10.18502/ijrm.v20i6.11439. eCollection 2022 Jun. Int J Reprod Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35958959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D receptor gene FokI, TaqI, BsmI, and ApaI polymorphisms and susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis: a meta-analysis.Genet Mol Res. 2015 Aug 7;14(3):9118-29. doi: 10.4238/2015.August.7.21. Genet Mol Res. 2015. PMID: 26345844
-
Vitamin D receptor ApaI, TaqI, BsmI, and FokI polymorphisms and psoriasis susceptibility: an updated meta-analysis.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019 Jul;44(5):498-505. doi: 10.1111/ced.13823. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30474246
Cited by
-
ASSOCIATION OF RS2435357 AND RS1800858 POLYMORPHISMS IN RET PROTO-ONCOGENE WITH HIRSCHSPRUNG DISEASE: SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS.Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2019 Oct 21;32(3):e1448. doi: 10.1590/0102-672020190001e1448. eCollection 2019. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2019. PMID: 31644668 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in IL-1A RS1800587, IL-1B RS1143634 and Vitamin D Receptor Rs731236 in Stage III Grade B/C Periodontitis.Balkan J Med Genet. 2023 Mar 1;25(1):51-60. doi: 10.2478/bjmg-2022-0005. eCollection 2022 Jun. Balkan J Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 36880040 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the CXCL12 rs1801157 Polymorphism with Breast Cancer Risk: A Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Mar 1;25(3):767-776. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.3.767. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 38546059 Free PMC article.
-
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium in Meta-Analysis Studies and Large-Scale Genomic Sequencing Era.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Jul 1;25(7):2229-2235. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.7.2229. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39068553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of VDR polymorphisms and postmenopausal osteoporosis.Endocr Connect. 2020 Oct;9(9):882-889. doi: 10.1530/EC-20-0296. Endocr Connect. 2020. PMID: 32738125 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
