Evaluation of physicochemical properties as supporting information on quality control of raw materials and veterinary pharmaceutical formulations
- PMID: 29922485
- PMCID: PMC6004627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2018.01.001
Evaluation of physicochemical properties as supporting information on quality control of raw materials and veterinary pharmaceutical formulations
Abstract
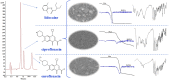
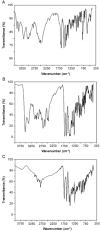
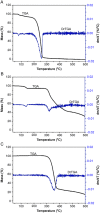
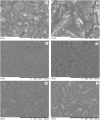
This study aimed to show that the physicochemical proprieties obtained by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetry (TG), and scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) can be useful tools for evaluating the quality of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and pharmaceutical products. In addition, a simple, sensitive, and efficient method employing HPLC-DAD was developed for simultaneous determination of lidocaine (LID), ciprofloxacin (CFX) and enrofloxacin (EFX) in raw materials and in veterinary pharmaceutical formulations. Compounds were separated using a Gemini C18 (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) Phenomenex® column, at a temperature of 25 °C, with a mobile phase containing 10 mM of phosphoric acid (pH 3.29): acetonitrile (85.7:14.3, v/v) and a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min. Physicochemical characterization by TG, FTIR, and SEM of raw materials of LID, CFX, and EFX provided information useful for the evaluation, differentiation, and qualification of raw materials. Finally, the HPLC method was proved to be useful for evaluation of raw material and finished products, besides satisfying the need for an analytical method that allows simultaneous determination of EFX, CFX, and LID, which can also be extended to other matrices and applications.
Keywords: HPLC; Physicochemical characterization; Quality control; Raw material; Veterinary pharmaceutical formulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HPLC residues of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in eggs of laying hens.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1997 May;8(4):253-6. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(97)00018-6. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1997. PMID: 18611811
-
Stability-Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Enrofloxacin and Its Degradation Products in Tablet Dosage Forms.J Anal Methods Chem. 2015;2015:735145. doi: 10.1155/2015/735145. Epub 2015 Jan 29. J Anal Methods Chem. 2015. PMID: 25705547 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous determination of 11 antibiotics and their main metabolites from four different groups by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array-fluorescence (HPLC-DAD-FLD) in human urine samples.Talanta. 2010 May 15;81(3):871-80. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2010.01.031. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Talanta. 2010. PMID: 20298867
-
Analytical Approaches to the Characterization of Solid Drug Delivery Systems with Porous Adsorbent Carriers.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(33):3956-3972. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180212120908. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29436989 Review.
-
Characterization of pharmaceutically relevant materials at the solid state employing chemometrics methods.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jan 5;147:538-564. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.06.017. Epub 2017 Jun 15. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 28666554 Review.
Cited by
-
HPMC/PVP K90 Dissolving Microneedles Fabricated from 3D-Printed Master Molds: Impact on Microneedle Morphology, Mechanical Strength, and Topical Dissolving Property.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;16(4):452. doi: 10.3390/polym16040452. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399830 Free PMC article.
-
Bilayer Mucoadhesive Buccal Film for Mucosal Ulcers Treatment: Development, Characterization, and Single Study Case.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jul 11;12(7):657. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12070657. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32664574 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Study for the Preparation of Transmucosal or Transdermal Patches with Acyclovir and Lidocaine.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Oct 19;13(20):3596. doi: 10.3390/polym13203596. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685355 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of iontophoresis-assisted transdermal delivery of bupivacaine and lidocaine as anesthetic drugs.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Feb;15(2):688-699. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01627-5. Epub 2024 May 23. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 38782881
-
Development of Dermal Lidocaine Nanosuspension Formulation by the Wet Milling Method Using Experimental Design: In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 18;9(52):50992-51008. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05296. eCollection 2024 Dec 31. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39758633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ICH, International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, 〈http://www.ich.org/home.htlm〉 (Accessed 16 September 2016).
-
- Gomes A.P.B., Correia L.P., da Silva Simoes M.O. Development of thermogravimetric method for quantitative determination of ketoconazole. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008;91:317–321.
-
- Lappalainen M., Karppinen M. Techniques of differential scanning calorimetry for quantification of low contents of amorphous phases. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010;102:171–180.
-
- Tanase C., Odochian L., Apostolescu N. TG-FTIR analysis applied to the study of thermal behaviour of some edible mushrooms. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011;103:1079–1085.
-
- Wesolowski M., Szynkaruk P., Makurat E. DSC and IR as supporting tools for identification of methylxanthines in solid dosage forms of drugs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012;109:807–815.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

