Evaluation of physicochemical properties as supporting information on quality control of raw materials and veterinary pharmaceutical formulations
- PMID: 29922485
- PMCID: PMC6004627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2018.01.001
Evaluation of physicochemical properties as supporting information on quality control of raw materials and veterinary pharmaceutical formulations
Abstract
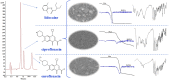
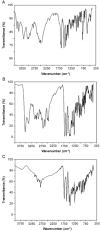
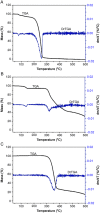
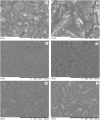
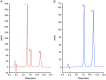
This study aimed to show that the physicochemical proprieties obtained by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetry (TG), and scanning electronic microscopy (SEM) can be useful tools for evaluating the quality of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and pharmaceutical products. In addition, a simple, sensitive, and efficient method employing HPLC-DAD was developed for simultaneous determination of lidocaine (LID), ciprofloxacin (CFX) and enrofloxacin (EFX) in raw materials and in veterinary pharmaceutical formulations. Compounds were separated using a Gemini C18 (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 µm) Phenomenex® column, at a temperature of 25 °C, with a mobile phase containing 10 mM of phosphoric acid (pH 3.29): acetonitrile (85.7:14.3, v/v) and a flow rate of 1.5 mL/min. Physicochemical characterization by TG, FTIR, and SEM of raw materials of LID, CFX, and EFX provided information useful for the evaluation, differentiation, and qualification of raw materials. Finally, the HPLC method was proved to be useful for evaluation of raw material and finished products, besides satisfying the need for an analytical method that allows simultaneous determination of EFX, CFX, and LID, which can also be extended to other matrices and applications.
Keywords: HPLC; Physicochemical characterization; Quality control; Raw material; Veterinary pharmaceutical formulation.
Figures
References
-
- ICH, International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, 〈http://www.ich.org/home.htlm〉 (Accessed 16 September 2016).
-
- Gomes A.P.B., Correia L.P., da Silva Simoes M.O. Development of thermogravimetric method for quantitative determination of ketoconazole. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008;91:317–321.
-
- Lappalainen M., Karppinen M. Techniques of differential scanning calorimetry for quantification of low contents of amorphous phases. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010;102:171–180.
-
- Tanase C., Odochian L., Apostolescu N. TG-FTIR analysis applied to the study of thermal behaviour of some edible mushrooms. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011;103:1079–1085.
-
- Wesolowski M., Szynkaruk P., Makurat E. DSC and IR as supporting tools for identification of methylxanthines in solid dosage forms of drugs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012;109:807–815.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

