Treatment of Dimpling from Cellulite
- PMID: 29922557
- PMCID: PMC5999441
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000001771
Treatment of Dimpling from Cellulite
Abstract
Background: Cellulite can be seen on the skin in widespread alterations of the skin surface and dimpling. The purpose of this study was to assess the effectiveness and safety of the manual subcision technique to treat dimpling from cellulite, using a specific class IIA medical device (Celluerase).
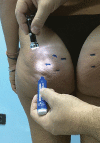
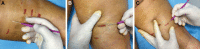
Methods: The multi-center observational study assessed 200 women treated in a single session for different dimpling, using manual subcision administered by Celluerase. Aesthetic outcomes were evaluated by the authors, and the patients assessed satisfaction levels.
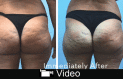
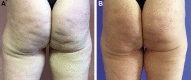
Results: Two hundred women between 20 and 55 years were treated. The medical evaluation of patients saw improvements with an average score of 8.1, whereas the subjective evaluation by patients gave an average improvement score of 7.8. Adverse events were reported.
Discussion: Women have septa orientation at right angels to the skin surface, and those with cellulite have an irregular septa conformation, with some septa being hypertrophic-thickened, and others being narrowed-lysed. Magnetic resonance imaging has confirmed that cellulite depressions are associated with a significant increase of thickness of underlying subcutaneous fibrous septa. Subcision has immediate results because it eliminates traction on the skin.
Conclusion: The study has shown the effectiveness and safety of the manual subcision in the treatment of dimpling. The device used, designed specifically for this technique, has shown itself to be very helpful and effective in terms of practical use, aesthetic outcome and safety, with various advantages compared with other commonly used devices.
Figures






References
-
- Nürnberger F, Müller G. So-called cellulite: an invented disease. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1978;4:221–229.. - PubMed
-
- Rossi AB, Vergnanini AL. Cellulite: a review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000;14:251–262.. - PubMed
-
- Hexsel DM. Body Repair. Women’s Dermatology. 2001:Nova Iorque, N.Y.: Parthenon Publishing; 586–595..
-
- Querleux B. Magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy of skin and subcutis. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2004;3:156–161.. - PubMed
-
- Mirrashed F, Sharp JC, Krause V, et al. Pilot study of dermal and subcutaneous fat structures by MRI in individuals who differ in gender, BMI, and cellulite grading. Skin Res Technol. 2004;10:161–168.. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
