New Method for Insomnia Mongolian Mind-Body Interactive Psychotherapy in the Assessment of Chronic Insomnia: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 29923046
- PMCID: PMC11343965
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-018-0726-9
New Method for Insomnia Mongolian Mind-Body Interactive Psychotherapy in the Assessment of Chronic Insomnia: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Introduction: Insomnia is a common clinical complaint, and if not addressed it can increase the risk of developing other underlying diseases such as hypertension, depression and anxiety. The use of Mongolian mind-body interactive therapy as a comprehensive psychotherapeutic approach in chronic insomnia has been shown in this retrospective study.
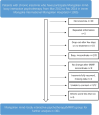
Methods: Subjects who had suffered insomnia for more than 1 month participated in the Mongolian mind-body interactive psychotherapy program between June 2012 and February 2014. They were interviewed by telephone at least 10 months before participating in the program. Their sleep was assessed using the Athens insomnia scale. Descriptive statistics, ANOVA and regression analysis were used for data analysis by SPSS software.
Results: Mongolian mind-body interactive psychotherapy significantly improved sleeping conditions. In ANOVA analysis, both short- and long-term outcomes were significantly affected by the treatment period. Patients who previously took medication and pre-treatment sleeping condition (ASI score) had a significant influence on long-term outcomes, as well as treatment time related to the duration of insomnia.
Conclusion: Mongolian mind-body interactive psychotherapy is a new method for insomnia, and narrative therapy and hypnotic methods together improve the sleeping condition, However, a further controlled randomized clinical study is needed to understand the efficacy.
Keywords: Chronic insomnia; Hypnosis; Mongolian mind–body interactive psychotherapy; Narrative therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors (Nagongbilige He, Wu Lan, Aruna Jiang, Haserden Jia, Shuzhi Bao, Longmei Bao, Altansha Qin, Orgel Bao, Shinjiltu Bao, Nandin Wang, Suyaltu Bao, Shuangfu Dai, Sarula Bao and Sarnai Arlud) have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical