Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 29923184
- PMCID: PMC6513124
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001190.pub3
Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia in older people. One approach to symptomatic treatment of Alzheimer's disease is to enhance cholinergic neurotransmission in the brain by blocking the action of the enzyme responsible for the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This can be done by a group of drugs known as cholinesterase inhibitors. Donepezil is a cholinesterase inhibitor.This review is an updated version of a review first published in 1998.
Objectives: To assess the clinical efficacy and safety of donepezil in people with mild, moderate or severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease; to compare the efficacy and safety of different doses of donepezil; and to assess the effect of donepezil on healthcare resource use and costs.
Search methods: We searched Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement's Specialized Register, MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO and a number of other sources on 20 May 2017 to ensure that the search was as comprehensive and up-to-date as possible. In addition, we contacted members of the Donepezil Study Group and Eisai Inc.
Selection criteria: We included all double-blind, randomised controlled trials in which treatment with donepezil was administered to people with mild, moderate or severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease for 12 weeks or more and its effects compared with those of placebo in a parallel group of patients, or where two different doses of donepezil were compared.
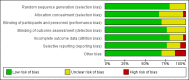
Data collection and analysis: One reviewer (JSB) extracted data on cognitive function, activities of daily living, behavioural symptoms, global clinical state, quality of life, adverse events, deaths and healthcare resource costs. Where appropriate and possible, we estimated pooled treatment effects. We used GRADE methods to assess the quality of the evidence for each outcome.
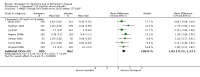
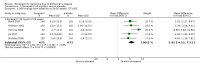
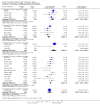
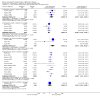
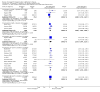
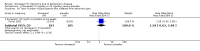
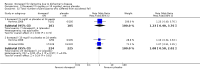
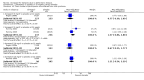
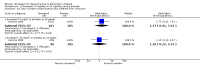
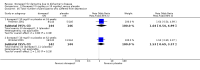
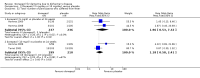
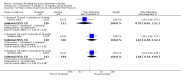
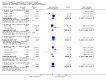
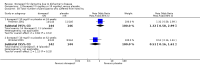
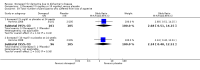
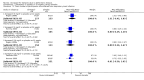
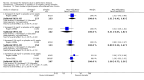
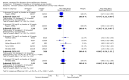
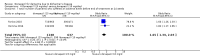
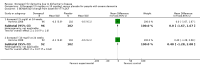
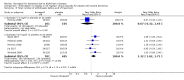
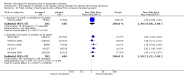
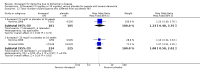
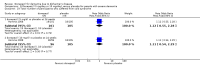
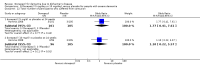
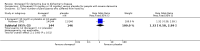
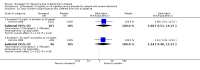
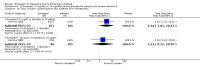
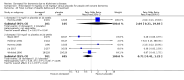
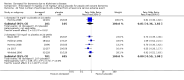
Main results: Thirty studies involving 8257 participants met the inclusion criteria of the review, of which 28 studies reported results in sufficient detail for the meta-analyses. Most studies were of six months' duration or less. Only one small trial lasted 52 weeks. The studies tested mainly donepezil capsules at a dose of 5 mg/day or 10 mg/day. Two studies tested a slow-release oral formulation that delivered 23 mg/day. Participants in 21 studies had mild to moderate disease, in five studies moderate to severe, and in four severe disease. Seventeen studies were industry funded or sponsored, four studies were funded independently of industry and for nine studies there was no information on source of funding.Our main analysis compared the safety and efficacy of donepezil 10 mg/day with placebo at 24 to 26 weeks of treatment. Thirteen studies contributed data from 3396 participants to this analysis. Eleven of these studies were multicentre studies. Seven studies recruited patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease, two with moderate to severe, and four with severe Alzheimer's disease, with a mean age of about 75 years. Almost all evidence was of moderate quality, downgraded due to study limitations.After 26 weeks of treatment, donepezil compared with placebo was associated with better outcomes for cognitive function measured with the Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive (ADAS-Cog, range 0 to 70) (mean difference (MD) -2.67, 95% confidence interval (CI) -3.31 to -2.02, 1130 participants, 5 studies), the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score (MD 1.05, 95% CI 0.73 to 1.37, 1757 participants, 7 studies) and the Severe Impairment Battery (SIB, range 0 to 100) (MD 5.92, 95% CI 4.53 to 7.31, 1348 participants, 5 studies). Donepezil was also associated with better function measured with the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study activities of daily living score for severe Alzheimer's disease (ADCS-ADL-sev) (MD 1.03, 95% CI 0.21 to 1.85, 733 participants, 3 studies). A higher proportion of participants treated with donepezil experienced improvement on the clinician-rated global impression of change scale (odds ratio (OR) 1.92, 95% CI 1.54 to 2.39, 1674 participants, 6 studies). There was no difference between donepezil and placebo for behavioural symptoms measured by the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) (MD -1.62, 95% CI -3.43 to 0.19, 1035 participants, 4 studies) or by the Behavioural Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease (BEHAVE-AD) scale (MD 0.4, 95% CI -1.28 to 2.08, 194 participants, 1 study). There was also no difference between donepezil and placebo for Quality of Life (QoL) (MD -2.79, 95% CI -8.15 to 2.56, 815 participants, 2 studies).Participants receiving donepezil were more likely to withdraw from the studies before the end of treatment (24% versus 20%, OR 1.25, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.50, 2846 participants, 12 studies) or to experience an adverse event during the studies (72% vs 65%, OR 1.59, 95% 1.31 to 1.95, 2500 participants, 10 studies).There was no evidence of a difference between donepezil and placebo for patient total healthcare resource utilisation.Three studies compared donepezil 10 mg/day to donepezil 5 mg/day over 26 weeks. The 5 mg dose was associated with slightly worse cognitive function on the ADAS-Cog, but not on the MMSE or SIB, with slightly better QoL and with fewer adverse events and withdrawals from treatment. Two studies compared donepezil 10 mg/day to donepezil 23 mg/day. There were no differences on efficacy outcomes, but fewer participants on 10 mg/day experienced adverse events or withdrew from treatment.
Authors' conclusions: There is moderate-quality evidence that people with mild, moderate or severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease treated for periods of 12 or 24 weeks with donepezil experience small benefits in cognitive function, activities of daily living and clinician-rated global clinical state. There is some evidence that use of donepezil is neither more nor less expensive compared with placebo when assessing total healthcare resource costs. Benefits on 23 mg/day were no greater than on 10 mg/day, and benefits on the 10 mg/day dose were marginally larger than on the 5 mg/day dose, but the rates of withdrawal and of adverse events before end of treatment were higher the higher the dose.
Conflict of interest statement
Jacqueline Birks: none known Richard Harvey: none known
Figures










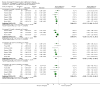
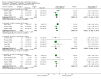





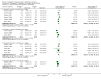













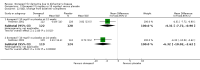










































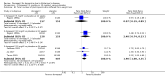
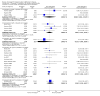

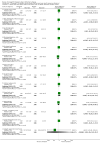





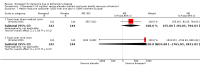
























































































































Update of
-
Donepezil for dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006 Jan 25;(1):CD001190. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001190.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 18;6:CD001190. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001190.pub3. PMID: 16437430 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
AD2000 {published data only}
-
- AD2000 Collaborative Group. Long‐term donepezil treatment in 565 patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD2000): randomised double‐blind trial. Lancet 2004;363:2105‐15. - PubMed
-
- Bentham P, Gray R, Hill R, Sellwood E, Courtney C. Twelve week response to cholinesterase inhibitors dose not predict future benefit the AD2000 trial experience. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:337.
-
- Lendon CL. Determination of responses to anticholinesterase therapy in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. 8th International Conference on Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders; 2002 July 20‐25, Stockholm, Sweden: Abstract No 1287. 2002.
-
- Roberts N. A reliable assessment of the efficacy and safety of donepezil and aspirin in Alzheimer's disease (AD2000). National Research Register 2001.
-
- Schneider LS. AD2000: donepezil in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 2004;363(9427):2100‐1. - PubMed
Black 2007 {published data only}
-
- Black S, Li HL, McRae T, Richardson S. Treatment of severe Alzheimer's disease with donepezil: results from a 24‐week, multinational, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Neurology 2006;66(5):A347.
-
- Black S, Li Honglang, McRae T, Richardson S. Donepezil treatment of severe Alzheimer's disease: results from a 24‐week, multinational, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial. Poster Presented at the Geneva Springfield Conference April 2006.
-
- Black SE, Doody R, Li H, McRae T, Jambor KM, Xu Y, et al. Donepezil preserves cognition and global function in patients with severe Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2007;69(5):459‐69. - PubMed
-
- Pfizer. E2020‐A001‐315: a 24 week multinational RCT evaluating the efficacy and safety of donepezil in severe AD. www.marc.soton.ac.uk/Research%20Page.htm.
-
- Richardson S. A 24 week, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled evaluation of the safety and efficacy of donepezil hydrochloride (E2020) in patients with severe Alzheimer's disease followed by a 12 week open‐label extension period. www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct/show/NCT00096473 2004.
Burns 1999 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bayer AJ, Rossor M, Hecker J, Gauthier S, Burns A, Petite H, et al. International Donepezil Study Group. Donepezil improves functional activity in patients with Alzheimer's disease. 21st Collegium Internationale Neuro Psychopharmacologicum; 1998 July 12‐16, Glasgow, Scotland. 1998. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Burns A, Gauthier S, Perdomo C. Efficacy and safety of donepezil over 3 years: an open‐label, multicentre study in patients with Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;22(8):806‐12. - PubMed
-
- Burns A, Rossor M, Hecker J, Gauthier S, Petit H, Möller H‐J, et al. International Donepezil Study Group. The effects of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease ‐ results from a multinational trial. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 1999;10(3):237‐44. - PubMed
-
- Gauthier S, Rosser M, Hecker J, Petite H, Rogers S, Mohr E, et al. Donepezil produces both clinical global and cognitive test improvement in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 151st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1998 May 30‐June 4, Toronto, Canada 1998. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Gauthier S, Rossor M, Hecker J. Results from a multinational phase III clinical trial of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease. Poster presentation at 5th International Geneva/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy. April 15‐18 1998.
Farlow 2010 {published data only}
-
- Doody RS, Geldmacher DS, Farlow MR, Sun Y, Moline M, Mackell J. Efficacy and safety of donepezil 23 mg versus donepezil 10 mg for moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease: a subgroup analysis in patients already taking or not taking concomitant memantine. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2012;33(2‐3):164‐73. - PubMed
-
- Doody RS, Ramos H, Faison W, Zou H. Efficacy and safety of donepezil 23 mg/d vs. donepezil 10 mg/d in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: impact of concomitant memantine use. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2011 Annual Scientific meeting of the American Geriatrics Society, National Harbor, MD, USA 2011.
-
- Farlow M, Richardson S, Mackell J, Sun Y. Long‐term safety and tolerability of donepezil 23 MG in patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease: an 18‐month analysis. Alzheimer's and Dementia 2011 Alzheimer's Association International Conference, Paris, France. 2011.
Feldman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Feldman H. Therapeutic benefits of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor therapy in the moderate to severe stage of Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; 2000 Apr 5‐8, Stockholm 2000:59.
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Emir B, Mastey V, et al. Donepezil treatment benefits caregivers of patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease (AD). European Journal of Neurology 2002;9(Suppl 2):34.
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Emir B, Mastey V, et al. and the Donepezil Study Group. Efficacy of donepezil on maintenance of activities of daily living in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease and the effect on caregiver burden.. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51:737‐44. - PubMed
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Hux M, Emir B, et al. Improved health outcomes with donepezil in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease are associated with economic benefits. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:285.
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Hux M, Xu Y, et al. Donepezil MSAD Study Investigators Group. Economic evaluation of donepezil in moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2004;63(4):644‐50. - PubMed
Hegerl 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hegerl U, Mergl R, Henkel V, Gallinat J, Kotter G, Muller Siecheneder F, et al. Kinematic analysis of the effects of donepezil hydrochloride on hand motor function in patients with Alzheimer dementia. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;23(2):214‐6. - PubMed
Homma 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Homma A, Imai Y, Hariguchi S, Hasegawa K, Kameyama M, Nishimura T. Late phase II clinical study of acetyl cholinesterase inhibitor E2020 in patients with Alzheimer‐type dementia. Clinical Evaluation 1998;26(2):251‐84.
Homma 2000 {published data only}
-
- Homma A, Takeda M, Imai Y, Udaka F, Hasegawa K, Kameyama M, et al. E2020 Study Group. Clinical efficacy and safety of donepezil on cognitive and global function in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a 24‐week, multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study in Japan. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2000; Vol. 11, issue 6:299‐313. - PubMed
Homma 2008 {published data only}
-
- Homma A, Arimoto I, Kaidoji K, Ohbayashi T, Ozawa H. Treatment of severe Alzheimer's disease with donepezil: results from a 24 week, parallel, placebo‐controlled study in Japan. 10th International Conference on Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders, Madrid, July 2006. 2006.
-
- Homma A, Imai Y, Tago H, Asada T, Shigeta M, Iwamoto T, et al. Donepezil treatment of patients with severe Alzheimer's disease in a Japanese population: results from a 24‐week, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized trial. Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008;25(5):399‐407. - PubMed
-
- Homma A, Imai Y, Tago H, Asada T, Shigeta M, Iwamoto T, et al. Long‐term safety and efficacy of donepezil in patients with severe Alzheimer's disease: results from a 52‐week, open‐label, multicenter, extension study in Japan. Dementia and Geritatric Congitive Disorders 2009;27(3):232‐9. - PubMed
Homma 2016 {published data only}
-
- Homma A, Atarashi H, Kubota N, Nakai K, Takase T. Efficacy and safety of sustained release donepezil high dose versus immediate release donepezil standard dose in Japanese patients with severe Alzheimer's disease: a randomized, double‐blind trial. Journal of Alzheimer's disease 2016;52(1):345‐57. - PubMed
Howard 2007 {published data only}
-
- Howard RJ, Juszczak E, Ballard CG, Bentham P Brown RG, Bullock R, et al. CALM‐AD Trial Group. Donepezil for the treatment of agitation in Alzheimer's disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357(14):1382‐92. - PubMed
-
- Pelosi A. Donepezil is no more effective than placebo for agitation in people with Alzheimer's disease. Evidence‐Based Mental Health 2008;11(3):84. - PubMed
Jia 2017 {published data only}
-
- Jia JP, Wei CB, Jia LF, Tang Y, Liang JH, Zhou AH, et al. Efficacy and safety of donepezil in Chinese patients with severe Alzheimer's disease: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Alzheimer's disease 2017;56(4):1495‐504. - PubMed
Krishnan 2003 {published data only}
-
- Anon. No title. Eisai Inc.
-
- Krishnan KR, Charles HC, Doraiswamy PM, Mintzer J, Weisler R, Yu X, et al. Randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of the effects of donepezil on neuronal markers and hippocampal volumes in Alzheimer's disease. The American Journal of Psychiatry 2003;160(11):2003‐11. - PubMed
Lebert 1999 {published data only}
-
- Robert P, Lebert F, Goni S, Touchon J, Vincent S, ARIAL Study Investigators Collaborative Group. The impact on caregiver distress of donepezil treatment of patients with mild Alzheimer's disease. Quality Research in Dementia; 19‐22 November, 2000, London. 2000.
-
- Robert PH, Lebert F, Goni S, Touchon J, ARIAL Study Investigators Collaborative Group. The impact of caregiver distress of donepezil treatment of patients with mild Alzheimer's disease. 152nd Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1999 May 15‐20, Washington DC. 1999. [MEDLINE: ]
Maher‐Edwards 2011 {published data only}
-
- Maher‐Edwards G, Dixon R, Hunter J, Gold M, Hopton G, Jacobs G, et al. SB‐742457 and donepezil in Alzheimer's disease: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2011;26(5):536‐44. - PubMed
-
- Maher‐Edwards G, Zvartau‐Hind M, Davies J, Alexander K, Schronen J, Boswell D, et al. Effects of 6‐month monotherapy treatment with the 5HT6 receptor antagonist SB 742457 or donepezil in subjects with mild‐to‐moderate Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Association International Conference, Paris, France. 2011.
Mazza 2006 {published data only}
-
- Korczyn AD. Comments on the article by Mazza et al. concerning Ginkgo biloba and donepezil: a comparison in the treatment of Alzheimer's dementia in a randomized placebo‐controlled double‐blind study. European Journal of Neurology 2007;14(9):e9. - PubMed
-
- Mazza M, Capuano A, Bria AP, Mazza S. Letter to the editor. European Journal of Neurology 2007;14(9):e10.
-
- Mazza M, Capuano A, Bria P, Mazza S. Ginkgo biloba and donepezil: a comparison in the treatment of Alzheimer's dementia in a randomized placebo‐controlled double‐blind study. European Journal of Neurology 2006;13(9):981‐85. - PubMed
Mohs 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ebell M. Does donepezil help patients with moderate Alzheimer's dementia preserve their ability to function independently?. Evidence Based Practice 2002.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni J, Perdomo C, Pratt R, et al. Donepezil preserves activities of daily living in Alzheimer's disease patients: results from a one‐year placebo‐controlled functional survival study. Neurology 2000;54(Suppl 3):A415.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni J, Rogers S, Perdomo C, et al. Donepezil preserves functional status and improves cognition in Alzheimer's disease patients: results from a 1‐year prospective placebo‐controlled study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2000;48(8):S46.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni JR, Rogers SL, Perdomo CA, et al. Donepezil preserves functional status in Alzheimer's disease patients: results from a 1‐year prospective placebo‐controlled attrition study. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 1999;9(Suppl 5):S328.
-
- Mohs R, Doody R, Morris J, Ieni JR, Rogers SL, Perdomo CA, et al. Donepezil preserves functional status in Alzheimer's disease patients: results from a 1‐year prospective placebo‐controlled study. Quality Research in Dementia Conference; 2000 November 19‐22, London. 2000.
Moraes 2006a {published data only}
-
- Moraes W, Poyares D, Sukys‐Claudino L, Guilleminault C, Tufik S. Donepezil improves obstructive sleep apnoea in Alzheimer disease: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Chest 2008;133(3):677‐83. - PubMed
-
- Moraes W, Sukys‐Claudino L, Poyares D, Guilleminault C, Tufik S. Donepezil improves oxygen desaturation in patients with alzheimer's disease and obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Medicine 2006;7(S47):368.
Moraes 2006b {published data only}
-
- Moraes W dos S, Poyares DR, Guilleminault C, Ramos LR, Bertolucci PH, Tufik S. The effect of donepezil on sleep and REM sleep EEG in patients with Alzheimer disease: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. Sleep 2006;29(2):199‐205. - PubMed
Rogers 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Friedhoff LT, Ieni JR, Rogers SL, Pratt RD. Donepezil provides long‐term clinical benefits for patients with Alzheimer's Disease. Proceedings of the 21st Collegium Internationale Neuro psychopharmacologicum;1998 July 12‐16, Glasgow, Scotland 1998:ABSTRACT REF: PW11017. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Friedhoff LT, Rogers SL. Correlation between the clinical efficacy of donepezil HCL (E2020) and red blood cell (RBC) acetylcholinesterase (ACHE) inhibition in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 98th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics; 1997 March 5‐8, San Diego. UK: Medical Education Network, 1997; Vol. 2:6‐7.
-
- Rogers S, Perdomo C, Friedhoff L. Clinical benefits are maintained during long‐term treatment of Alzheimer's disease with the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, E2020. Proceedings of the 8th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1995 September 30‐October 4, Venice 1995a. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Rogers SL, Doody RS, Pratt RD, Ieni JR. Long‐term efficacy and safety of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: final analysis of a US multicentre open‐label study. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2000; Vol. 10, issue 3:195‐203. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. E2020 improves cognition and quality of life in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimers Disease: results of a phase II trial. Proceedings of the 46th Annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. 1994 May 1‐7, Washington DC 1994; Vol. 44, issue Suppl 2:A165.
Rogers 1998a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Doody RS, Geldmacher DS, Gordon B, Perdomo CA, Pratt RD, Donepezil Study Group. Open‐label, multicenter, phase 3 extension study of the safety and efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology 2001;58(3):427‐33. - PubMed
-
- Pratt RD, Perdomo CA, Ieni JK. Long‐term safety and tolerability of donepezil: results from a phase iii extension trial of patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease. European Journal of Neurology 1999;6(Suppl 3):116. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Rogers SL. Donepezil new clinical trials support long term use. Sixth International Stockholm/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer Therapy; 2000 April 5‐8, Stockholm. 2000:133.
-
- Rogers SL, Doody RS, Mohs RC, Friedhoff LT, the Donepezil Study Group. Donepezil improves cognition and global function in Alzheimer disease. Archives of Internal Medicine 1998;158:1021‐31. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SL, Mohs RC, Friedhoff LT. Donepezil (E2020) improves cognition and function in patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease. Results from phase III trials. American Psychiatric Association 150th Annual Meeting, San Diego. 1997.
Rogers 1998b {published data only}
-
- Doody RS, Geldmacher DS, Gordon B, Perdomo CA, Pratt RD, Donepezil Study Group. Open‐label, multicenter, phase 3 extension study of the safety and efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology 2001;58(3):427‐33. - PubMed
-
- Feldman H, Gauthier S, Hecker J, Vellas B, Subbiah P, Whalen E, Donepezil MSAD Study Investigators Group. Erratum: a 24‐week, randomized, double‐blind study of donepezil in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease (Neurology (2001) 57 (613‐620)). Neurology 2001; Vol. 57, issue 11:2153. - PubMed
-
- Friedhoff LT, Rogers L. Donepezil lengthens time to loss of activities of daily living in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease ‐ results of a preliminary evaluation. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology. Boston. Neurology 1997;48(3):A100.
-
- Friedhoff LT, Rogers SL. Donepezil lengthens time to loss of activities of daily living and cognition in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1997 Sep 13‐17, Vienna, Austria 1997. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Friedhoff LT, Rogers SL. Donepezil maintains activities of daily living in patients with mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease: results of a retrospective analysis. European Journal of Neurology 1997;4(Suppl 1):S9.
Schindler 2004 {published data only}
-
- Schindler R, Corey‐Bloom J, Doody R, Zhang R, Ieni JR, Li H. Donepezil is safe and well tolerated in Alzheimer's disease patients, at doses of up to 20 mg/day. 8th Congress of the European Federation of the Neurological Sciences. Paris, France. September 4‐7, 2004. 2004.
-
- Schindler R, Zhang R, Ieni JR, Li H. Donepezil is safe and well tolerated in Alzheimer's disease patients, at doses of up to 20 mg/day. Neurobiology of Aging 2004;25(S2):195.
Seltzer 2004 {published data only}
-
- Seltzer B, Zolnouni P, Nunez M, Goldman R, Kumar D, Ieni J, et al. Erratum: efficacy of donepezil in early‐stage alzheimer disease: a randomized placebo‐controlled trial (Archives of Neurology (December 2004) 61 (1852‐1856)). Archives of Neurology 2005;62(5):825. - PubMed
-
- Seltzer B, Zolnouni P, Nunez M, Goldman R, Kumar D, Ieni J, et al. Donepezil 402 Study Group. Efficacy of donepezil in early‐stage Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurolology 2004;61:1852‐6. - PubMed
Study 205 {published data only}
-
- Anon. No title. Eisai Inc.
Study 306 {published data only}
-
- Anon. No title. Eisai Inc.
Tariot 2001 {published data only}
-
- Steinman MA, Covinsky KE, Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, et al. Donepezil for nursing home patients with dementia: a reinterpretation of the evidence. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(1):132‐33. - PubMed
-
- Tariot P, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Perdomo CA, Whalen E, Sovel MA, et al. Donepezil was well‐tolerated and enhanced cognition in nursing home patients with Alzheimer's disease. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1999;47:S3. - PubMed
-
- Tariot P, Perdomo CA, Whalen E, Sovel MA, Scham EM. Age is not a barrier to donepezil treatment of Alzheimer's disease in the long‐term care setting. International Psychogeriatrics 1999;11(Supplement 1):134.
-
- Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, Perdomo CA, Schwam EM, et al. A randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of Donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the nursing home setting. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001;49(12):1590‐9. - PubMed
-
- Tariot PN, Cummings JL, Katz IR, Mintzer J, Perdomo CA, Schwam EM, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease in the nursing home setting. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(1):133‐4. - PubMed
Tune 2003 {published data only}
-
- Tune L, Tiseo P, Hoffman J, Perdomo C, Votaw J, Rogers S, et al. PET in AD: Donepezil HCl (E2020) maintains functional brain activity in patients with Alzheimer's disease: results of a 24‐week study. 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 2001 February 23‐26 San Francisco. 2001.
-
- Tune L, Tiseo PJ, Ieni J, Perdomo C, Pratt RD, Votaw JR, et al. Donepezil HCl (E2020) maintains functional brain activity in patients with Alzheimer disease: results of a 24‐week, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;11(2):169‐77. - PubMed
-
- Tune LE, Tiseo PJ, Hoffman JM, Perdomo CA, Votow JR, Rogers SL, et al. Functional brain activity in Alzheimer's disease. 151st Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1998 May 30‐ June 4, Toronto. 1998:NR345. [MEDLINE: ]
Winblad 2001 {published data only}
-
- Engedal K, Soininen H, Verhey F, Waldemar G, Winblad B, Wimo A, et al. Donepezil improved or stabilized cognition over one year in patients with mild and moderate Alzheimer's disease. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000; Vol. 10, issue Suppl 3:S368. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Mastey V, Wimo A, Winblad B, Haglund A, Jacobson L, Miceli R, et al. An economic evaluation of donepezil in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: results of a one year, double‐blind, randomized trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001; Vol. 49, issue 4:S131.
-
- Mastey V, Wimo A, Winblad B, Haglund A, Jacobson L, Miceli R, et al. Donepezil reduces the time caregivers spend providing care: results of a one‐year, double‐blind, randomized trial in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 2001 Feb 23‐26, San Francisco 2001.
-
- Soininen H, Winblad B, Engedal K, Verhey F, Waldemar G, Wimo A, et al. Long term benefits of donepezil on ADLs in AD patients. Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Geriatric Society and the American Federation for Aging Research; 2000 May 17‐21, Nashville. 2000:171.
-
- Soininen H, Winblad B, Engedal K, Verhey F, Waldemar G, Wimo A, et al. Donepezil Nordic Study Group. Response to donepezil is not predicted by apolipoprotein E genotype and/or gender. World Alzheimer Congress; 2000 July 9‐13, Washington. 2000.
Winblad 2006 {published data only}
-
- Batsman S, Minthon L, Eeriksson S, Kilander L, Jansson‐Blixt C, Wetterholm A, et al. Study design and baseline patients characteristics in a randomized controlled trial of the efficacy and tolerability of donepezil in severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Eriksson S, Winblad B, Kilander L, Batsman S, Jansson‐Blixt C, Wetterholm A, et al. Efficacy of donepezil on secondary end points in a randomized, double‐blind placebo‐controlled study in severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Jelic V, Haglund A, Kowalski J, Langworth S, Winblad B. Donepezil treatment of severe Alzheimer's disease in nursing home settings. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008;26(5):458‐46. - PubMed
-
- Kilander L, Winblad B, Minthon L, Batsman S, Jansson‐Blixt C, Cronlund A, et al. Donepezil is well tolerated in patients with severe Alzheimer's disease. IPA 12th International Congress, Stockholm, Sweden, 20‐24 September 2005. 2005.
-
- Marder K. Donepezil in patients with severe Alzheimer's disease: double‐blind parallel‐group, placebo controlled study. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports 2006;6(5):364‐73. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ames 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ames D, Boada M, Sakka P, Triau E, Turcani P, Vagenas V, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease: findings from a large multinational experience study. 17th Alzheimer's Disease International Conference; 2001 October 25‐27, Christchurch, New Zealand. 2001:181.
AWARE {published data only}
-
- Johannsen P, Barcikowska M, Hasselbalch S, Ihl R, Karageorgiou C, Nunez M, et al. AWARE Study Group. Results from the pre‐randomization phase of the donepezil aware study further understanding the meaning of clinical benefit. 7th International Geneva/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer therapy, 2002 Apr 3‐6, Geneva. 2002:201.
-
- Johannsen P, Holub R, Jakab G, Jakobsen S, Kalisvaart CJ, Kozubski W, et al. Behavioral benefits with continued donepezil treatment in Alzheimer's disease patients. Neurobiology of Aging 2004;25(S2):20.
-
- Johannsen P, Salmon E, Hampel H, Xu Y, Richardson S, Qvitzau S, et al. AWARE Study Group. Assessing therapeutic efficacy in a progressive disease: a study of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease. CNS Drugs 2006;20(4):311‐25. - PubMed
-
- Johanssen O, Dautzenburg P, Heun R, Holub R, Jakab G, Kozubski W, et al. AWARE Study Group. Results from the pre‐randomization phase of the donepezil AWARE study: further understanding the meaning of "clinical benefit". 8th International Conference on Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders; 2002 July 20‐25, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:Abstract No 305.
-
- Johanssen P, Hasselbalch S, Jakab G, Kalisvaart CJ, Kozubski W, Kurz A, et al. Behavioral benefits with continued donepezil treatment in Alzheimer's disease patients. 8th Congress of the European Federation of the Neurological Sciences. Paris, France. September 4‐7, 2004. 2004.
Barak 2001 {published data only}
-
- Barak Y, Bodner E, Zemishlani H, Mirecki I, Aizenberg D. Donepezil for the treatment of behavioral disturbances in Alzheimer's disease: a 6‐month open trial. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2001;33:237‐41. - PubMed
Berger 2000 {published data only}
-
- Berger E, Sramko CA, Frölich L, Calabrese P. Donepezil provides relevant therapeutic benefits in different domains to real world patients with Alzheimer's disease. The 12th ENCP Congress European Neuropsychopharmacology, London, 2000. 2000; Vol. 10, issue S4:369.
-
- Sramko CA, Berger F, Calabrese P, Frölich L. Tolerability and safety of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease results from a post marketing surveillance study. The 12th ENCP Congress European Neuropsychopharmacology, London, 2000. 2000; Vol. 10, issue S4:368.
Birt 2002 {published data only}
-
- Birt AR, Fay S, Graham JE, Rockwood K. Recovery of intention as a novel effect on treating Alzheimer's disease with donepezil. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:595.
Borroni 2001 {published data only}
-
- Borroni B, Colciaghi F, Pastorino L, Pettenati C, Cottini E, Rozzini L, et al. Amyloid precursor protein in platelets of patients with Alzheimer disease: effect of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor treatment. Archives of Neurology 2001;58(3):442‐6. - PubMed
Brodaty 2000 {published data only}
-
- Boundy K, Brodaty H, Australian Donepezil Study Group, Barrington M, O'Leary M, Short K, et al. Efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease: findings from the Australian subset of a large multinational experience study. Proceedings of the 17th Alzheimer's Disease International Conference; 2001 Oct 25‐27, Christchurch, New Zealand. 2001.
-
- Brodaty H, Bahara R, Zhang R, O'Leary M, Short K, Barrington M. Efficacy and safety of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease preliminary findings from the Australian subset of a global clinical experience study. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;10(Suppl 4):S367.
Bullock 2000 {published data only}
-
- Bullock RA, Voss SE. The clinical utility of donepezil: from randomized clinical trials to practice. World Alzheimer Congress; 2000 July 9‐13, Washington. 2000.
Bullock 2001 {published data only}
-
- Blesa R, Bullock R, He Y, Bergman H, Gambina G, Meyer J, et al. Effect of butyrylcholinesterase genotype on the response to rivastigmine or donepezil in younger patients with Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics 2006;16(11):771‐4. - PubMed
-
- Bullock R, Bergman H, Touchon J, Gambina G, He Y, Nagel J, et al. Effect of age on response to rivastigmine or donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2006;22(3):483‐94. - PubMed
-
- Bullock R, Passmore F, Potocnik F, Hock C. The tolerability, ease of use and efficacy of donepezil and rivastigmine in Alzheimer's disease patients: a 12‐week, multinational, comparative study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001;49(4):S19.
-
- Bullock R, Wilkinson DG, Passmore P, Hopker SW, Smith R, Potocnik FC, et al. Caregiver and physician determination of satisfaction with and ease of use of donepezil and rivastigamine treatment in Alzheimer's disease patients. 17th Alzheimer's Disease International Conference; 2001 Oct 25‐27, Christchurch, New Zealand. 2001:39.
-
- Böttcher‐Buhler E. Well tolerated, effective and inexpensive therapy of Alzheimer's dementia with donepezil [Therapie der Alzheimer‐Demenz mit Donepezil: gut vertraglich, wirksam und kostengunstig]. Neurologie und Rehabilitation 2000;6(6):332‐3.
Cameron 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cameron I, Curran S, Newton P, Petty D, Wattis J. Use of donepezil for the treatment of mild‐moderate Alzheimer's disease: an audit of the assessment and treatment of patients in routine clinical practice. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;15(10):887‐91. - PubMed
Clary 2000 {published data only}
-
- Clary C, McRae T, Griesing T, Whalen E. The safety of donepezil and sertraline for the management of behavioral symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;3(Suppl 1):S267. [MEDLINE: ]
-
- Finkel S, McRae T, Burt T. Sertraline and donepezil demonstrate greater efficacy and similar tolerability compared to donepezil alone in non‐depressed patients with Alzheimer's disease. 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 2001 February 23‐26, San Francisco. 2001.
-
- McRae T, Griesing T, Whalen E. Donepezil and sertraline for the management of behavioral symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 2000;54(Suppl 3):A416‐7.
-
- McRae T, Griesing T, Whalen E. Effectiveness of donepezil on behavioural disturbances in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease patients. World Alzheimer Congress; 2000 July 9‐13, Washington. 2000.
-
- McRae T, Griesling T, Whalen E. Managing behaviour symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Annual Scientific Meeting of the American Geriatric Society and the American Federation for Aging Research; 2000 May 17‐21, Nashville. 2000:173.
Cumbo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cumbo E. Improvement in behavioral and psychiatric symptoms (BPSD) in patients with moderate‐to‐severe Alzheimer's disease by current antidementia treatments. Alzheimer's Association International Conference, Paris, France. 2011.
Cummings 2000 {published data only}
-
- Cummings JL, Donohue JA, Brooks RL. The relationship between donepezil and behavioral disturbances in patients with Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000;8(2):134‐40. - PubMed
DOMINO‐AD {published data only}
-
- Howard R, McShane R, Lindesay J, Ritchie C, Baldwin A, Barber R, et al. Nursing home placement in the Donepezil and Memantine in Moderate to Severe Alzheimer's Disease (DOMINO‐AD) trial: secondary and post‐hoc analyses. Lancet Neurology 2015; Vol. 14, issue 12:1171‐81. - PubMed
Dong 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dong GS, Li X, Jiang QH, Yang HQ. Effects of donepezil treatment on platelets alpha and beta secretase activities in Alzheimer's disease patients. Chinese Medical Journal 2011;91(47):3341‐5. - PubMed
Fillit 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fillit H, Hill JW, Futtertman R, Mastery V. Sustained donepezil therapy reduces healthcare costs in Alzheimer's disease. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:192.
Froelich 2000 {published data only}
-
- Froelich L, Gertz HJ, Heun R, Heuser I, Jendroska K, Kornhuber J, et al. Donepezil for Alzheimer's disease ‐ the Donald Study ‐ a multicenter 24 weeks clinical trial in Germany. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000;10(Suppl 3):S360. [MEDLINE: ]
Fuschillo 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fuschillo C, Pia S, Campana F, Pinto A, Simone L. Cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease: treatment with acetylcholinesterase inhibitor agents. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2001;33(Suppl 1):151‐8. - PubMed
Geldmacher 2003 {published data only}
-
- Finucane TE. Another advertisement for donepezil. Comments to the editor; reply Geldmacher. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2004;52(5):843‐6. - PubMed
-
- Geldmacher DS, Provenzano G, McRae T, Mastey V, Ieni JR. Donepezil is associated with delayed nursing home placement in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2003;51(7):937‐44. - PubMed
-
- Karlawish JH. Donepezil delay to nursing home placement study is flawed. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2004;52(5):845; author reply 845‐6. - PubMed
-
- Schneider LS, Qizilbash N. Delay in nursing home placement with donepezil. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2004;52(6):1024‐6; author reply 1026‐7. - PubMed
Ghorbani 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ghorbani A, Chitsaz A, Shishegar M, Akbari M. Evaluation of the effect of donepezil on cerebral blood flow velocity in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosciences (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia) 2010; Vol. 15, issue 3:172‐6. - PubMed
Greenberg 2000 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg SM, Tennis MK, Brown LB, Gomez‐Isla T, Hayden DL, Schoenfeld‐DA, et al. Donepezil therapy in clinical practice: a randomized crossover study. Archives of Neurology 2000;57:94‐9. - PubMed
Hampel 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hampel H, Berger F, Froelich L. Switching from other antidementive therapies to donepezil (Aricept): improvement of quality of life of Alzheimer patients in routine clinical use. The International Symposium on advances in Alzheimer therapy, 2002, Geneva. 2002:198.
Holmes 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hepple J. A study of the effects of donepezil on non‐cognitive symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the clinical characteristics of responders. National Research Register 2003.
-
- Holmes C. Non‐cognitive symptoms and response to donepezil. National Research Register 2000.
-
- Holmes C, Wilkinson D, Dean C, Vethanayagam S, Olivieri S, Langley A, et al. The efficacy of donepezil in the treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2004;63(2):214‐9. - PubMed
-
- Pandita‐Gunawardena D. Non‐cognitive symptoms and response to donepezil. National Research Register 2001.
Homma 1998a {published data only}
-
- Homma A, Imai Y, Hariguchi S, Hasegawa K, Kameyama M, Nishimura T. Late phase II clinical study of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor E2020 in patients with Alzheimer‐type dementia. Clinical Evaluation 1998;26:185‐207.
Homma 1998b {published data only}
-
- Homma A, Imai Y, Hariguchi S, Hasegawa K, Kameyama M, Nishimura T. Late phase II clinical study of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor E2020 in patients with Alzheimer‐type dementia. Clinical Evaluation 1998;26:209‐31.
Imai 1998a {published data only}
-
- Imai Y, Homma A, Hariguchi S, Hasegawa K, Kameyama M, Nishimura T. Early phase II clinical study of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor E2020 in patients with Alzheimer‐type dementia. Clinical Evaluation 1998;26:145‐64.
Imai 1998b {published data only}
-
- Imai Y, Homma A, Hariguchi S, Hasegawa K. Early phase II clinical study of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor E2020 in patients with Alzheimer‐type dementia. Clinical Evaluation 1998;26:165‐83.
Imai 1998c {published data only}
-
- Imai Y, Homma A, Hariguchi S, Hasegawa K, Kameyama M, Nishimura T. Late phase II clinical study of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor E2020 in patients with Alzheimer‐type dementia. Clinical Evaluation 1998;26:233‐50.
Janssen 2005 b {published data only}
-
- Janssen LP. A double‐blind, randomized pilot study to evaluate the effects of galantamine and donepezil on sleep and attention in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. ClinicalTrials.gov 2005. - PubMed
Kauffer 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kauffer D, Catt K, Pollock B, DeKosky S. Assessing the effects of donepezil in Alzheimer's patients and its impact on caregivers. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1998; Vol. 46:S66.
Kemp 2003 {published data only}
Leube 2002 {published data only}
-
- Leube D, Grodd W, Erb M, Henning W, Bartels M, Kircher T. Task related cortical areas are differentially activated in patients with Alzheimer's disease after a ten week treatment with donezepil. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:1548.
Lopez 2008 {published data only}
Maltz 2002 {published data only}
-
- Maltz J, Eberling J, Jagust W, Budinger T. Donepezil therapy enhances methacholine induced cutaneous vasodilation in Alzheimer's disease patients. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:318.
Matthews 2000 {published data only}
-
- Matthews HP, Korbey J, Wilkinson DG, Rowden J. Donepezil in Alzheimer's disease: eighteen month results from Southampton Memory Clinic. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2000; Vol. 15, issue 8:713‐20. - PubMed
McRae 1999 {published data only}
-
- McRae T, Orazem J. A large, community‐based trial of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1999; Vol. 47:S63.
McRae 2001a {published data only}
-
- McRae T, Knopman D, Duttagupta S, Ieni J, Provenzano G. Donepezil delays time to nursing home placement in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry; 2001 February 23‐26, San Francisco 2001a.
-
- McRae T, Knopman D, Mastey V, Ieni J, Provenzano G. Donepezil is strongly associated with delayed nursing home placement in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Neuroscience 2001; Vol. 187, issue Suppl 1:S536.
Mega 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mega MS, Masterman DM, O'Connor SM, Barclay TR, Cummings JL. The spectrum of behavioral responses to cholinesterase inhibitor therapy in Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology 1999; Vol. 56, issue 11:1388‐93. - PubMed
Mega 2001 {published data only}
-
- Mega MS, Manese M, Felix J, Tran N, O'Connor SM, Masterman DM, et al. Laboratory of Neuroimaging and Alzheimer's disease. Anterior cingulate activation occurs across cholinesterase inhibitor therapy in Alzheimer's disease. 10th congress of the international psychogeriatric association, Nice, France, September 9‐14, 2001 2001; Vol. 13, issue Suppl 2:S108.
Mega 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mega M, Dinov I, Manese M, Felix J, O'Connor S, Toga A, et al. Cerebral metabolic activation with cholinesterase inhibitor therapy in Alzheimer's disease. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:430.
Modrego 2010 {published data only}
-
- Modrego PJ, Fayed N, Errea JM, Rios C, Pina MA, Sarasa M. Memantine versus donepezil in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: a randomized trial with magnetic resonance spectroscopy. European Journal of Neurology 2010;17(3):405‐12. - PubMed
NCT00423228‐BRAINz {published data only}
-
- NCT00423228‐BRAINz. A randomised, double‐blind, double‐dummy, oral donepezil controlled study on the safety and efficacy of repeated monthly subcutaneous injections of a sustained‐release implant of ZT 1 in patients with moderate Alzheimer's disease. ClinicalTrials.gov 2007.
Nikolova 2001 {published data only}
-
- Nikolova G, Traykov L. Efficacy of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease ‐ results of 12‐week open clinical trial. Acta Medica Bulgarica 2001; Vol. 28:70‐5.
Nobili 2002 {published data only}
-
- Nobili F, Vitali P, Canfora M, Girtler N, Leo C, Mariani G, et al. Effects of long‐term donepezil therapy on rCBF of Alzheimer's patients. Clinical Neurophysiology 2002;113(8):1241‐8. - PubMed
Ollat 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ollat H, Laurent B, Bakchine S, Michel BF, Touchon J, Dubois B. Effects of the association of sulbutiamine with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor in early stage and moderate Alzheimer disease [Effets de l'association de la sulbutiamine à un inhibiteur de l'acétylcholinestérase dans les formes légères à modérées de la maladie d'Alzheimer]. L'Encéphale 2007;33(2):211‐5. - PubMed
Onofrj 2002 {published data only}
-
- Onofrj M, Thomas A, Luciano AL, Iacono D, Rollo A, D'Andreamatteo G, et al. Donepezil versus vitamin E in Alzheimer's disease: part 2: mild versus moderate‐severe Alzheimer's disease. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2002;25(4):207‐15. - PubMed
Onofrj 2003 {published data only}
-
- Onofrj M, Thomas A, Iacono D, Luciano AL, Iorio A. The effects of a cholinesterase inhibitor are prominent in patients with fluctuating cognition: a part 3 study of the main mechanism of cholinesterase inhibitors in dementia. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2003;26(5):239‐51. - PubMed
Parsa 2000 {published data only}
-
- Parsa MA, Poggi E, Barte L. Treatment of dementia patients with psychotic and behavioural symptoms with quetiapine and donepezil. Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 2000; Vol. 10, issue Suppl 3:S302. [MEDLINE: ]
Peng 2002 {published data only}
-
- Peng D, Xu X, Hou Q. The safety and efficacy of Aricept in patients with Alzheimer disease. Chinese Journal of Neurology 2002; Vol. 35, issue 1:19‐21.
Peng 2005 {published data only}
-
- Peng DT, Xu XH, Wang LN. Efficiency and safety assessment of donepezil for treating mild and moderate Alzheimer disease. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2005;9(13):170‐2.
Requena 2006 {published data only}
-
- Requena C, Maestu F, Campo P, Fernandez A, Ortiz T. Effects of cholinergic drugs and cognitive training on dementia: 2‐year follow‐up. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2006;22(4):339‐45. - PubMed
Richarz 2011 {published data only}
-
- Richarz U, Gaudig M, Schaeuble B, Zhang Z. Cognitive outcomes of patients with Alzheimer's disease treated with galantamine or donepezil: a randomized, double‐blind study. European Journal of Neurology 15th Congress of the EFNS, Budapest, Hungary. 2011.
Rocca 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rocca P, Cocuzza E, Marchiaro L, Bogetto F. Donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: long‐term efficacy and safety. Progress in Neuro‐psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 2002; Vol. 26, issue 2:369‐73. - PubMed
Rockwood 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rockwood K, Graham J, Fay S. Translating from regulatory measures to patients' daily lives an analysis of Alzheimer's disease treatment with donepezil. The 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:2034.
Rockwood 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rockwood K, Black S, Bedard MA, Tran T, Lussier I, TOPS Study Investigators. Specific symptomatic changes following donepezil treatment of Alzheimer's disease: a multi‐centre, primary care, open‐label study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;22(4):312‐19. - PubMed
Rodriguez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rodriguez G, Vitali P, Leo C, Cadi F, Girtler N, Nobili F. Quantitative EEG changes in Alzheimer patients during long‐term donepezil therapy. International Symposium on advances in Alzheimer therapy, 2002, Geneva 2002:239.
Rogers 1997 {published data only}
-
- Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. Donepezil is well tolerated at clinically effective doses for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Proceedings of the 10th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1997 September 13‐17, Vienna, Austria 1997. [MEDLINE: ]
Rogers 1997b {published data only}
-
- Friedhoff LT, Jeni R, Rogers SL, Pratt RD. Donepezil provides long term benefits for patients with Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Psychopharmacology 1999;2(Suppl 1):5175(PW11017).
-
- Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. Donepezil provides long‐term clinical benefits for patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). International Journal of Neurological Sciences 1997;150:296.
-
- Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. Long‐term efficacy and safety of donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: an interim analysis of the results of a US multicentre open label extension study. European Neuropsychopharmacology 1998;8:67‐75. - PubMed
-
- Rogers SL, Perdomo C, Friedhoff LT. Clinical benefits are maintained during long‐term treatment of Alzheimer's disease with the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor E2020. European Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 1995;5(3):386.
Rozzini 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rozzini L, Bargnani C, Bosio A, Chia F, Franzani S, Leonardi R, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are effective in real world patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease evidence from a large population treated with rivastigmine or donepezil. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:329.
-
- Rozzini L, Bargnani C, Bosio A, Chia F, Franzoni S, Leonardi R, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of rivastigmine and donepezil in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: results from a multicentre randomised trial. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden. 2002:240.
Rozzini 2007a {published data only}
-
- Rozzini L, Chilovi BV, Bertoletti E, Ghianda D, Conti M, Trabucchi M, et al. Serum albumin level interferes with the effect of donepezil in Alzheimer's disease. Aging Clinical Experimental Research 2008;20(6):509‐12. - PubMed
Rozzini 2007b {published data only}
-
- Rozzini L, Chilovi BV, Bertoletti E, Trabucchi M, Padovani, A. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and depressive symptoms in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. Clinical and Experimental Research 2007;19(3):220‐3. - PubMed
Salloway 2002 {published data only}
-
- Salloway S. A double blind randomized pilot study to evaluate the effects of galantamine and donepezil on sleep and attention and gastrointestinal GI tolerance in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease AD [Effects on sleep and attention of two currently marketed drugs for Alzheimer's disease]. Clinical Trials.gov 2002:1‐2.
Sampson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sampson EL, Raven PR, Ndhlovu PN, Vallance A, Garlick N, Watts J, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept) for reducing the incidence of postoperative delirium after elective total hip replacement. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;22(4):343‐9. - PubMed
Saumier 2007 {published data only}
-
- Saumier D, Murtha S, Bergman H, Phillips N, Whitehead V, Chertkow H. Cognitive predictors of donepezil therapy response in Alzheimer disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2007;24(1):28‐35. - PubMed
Shua‐Haim 2002a {published data only}
-
- Shua‐Haim J, Smith J, Amin S, Shua‐Haim V. Comparison of combination therapy with rivastigmine Exelon and donepezil Aricept versus rivastigmine alone for treatment of Alzheimer's disease safety tolerability and clinical experience after one year of treatment a cross section study. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:292.
Shua‐Haim 2002b {published data only}
-
- Shua‐Haim J, Smith J, Potel S. A head to study of donepezil Aricept rivastigmine Exlon and galantamine Reminyl for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease safety tolerability clinical and caregiver impression after 4‐5 months of treatment a prospective study. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:286.
Stewart 1998 {published data only}
-
- Stewart A, Phillips R, Dempsey G. Pharmacotherapy for people with Alzheimer's disease: a Markov‐cycle evaluation of five years' therapy using donepezil. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1998; Vol. 13, issue 7:445‐53. - PubMed
Tarraga 2006 {published data only}
Teipel 2006 {published data only}
-
- Teipel SJ, Drzezga A, Bartenstein P, Moller HJ, Schwaiger M, Hampel H. Effects of donepezil on cortical metabolic response to activation during (18)FDG‐PET in Alzheimer's disease: a double‐blind cross‐over trial. Psychopharmacology 2006;187(1):86‐94. - PubMed
Tessitore 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tessitore A, Iavarone A, Tessitore A. Donepezil in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease: follow‐up at 12 months in 40 treated patients. Nuova Rivista di Neurologia 2000; Vol. 10, issue 5:183‐6.
Tettamanti 2000 {published data only}
-
- Tettamanti M, Casilli D, Baldinetti F, Apollonio I, Ruffo P, Nobili A, et al. Donepezil Italian Global Impact Study (DIGIS). Proceedings of the World Alzheimer Congress; 2000 July 9‐13, Washington DC 2000.
Thal 2004 {published data only}
-
- Galasko DR, Gauthier S, Bennett D, Sano M, Kaye J, Marson D, et al. Impairment of activities of daily living in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment in an ADCS randomized clinical trial. 57th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, Miami Beach, April 2005. 2005:S15.001.
-
- Petersen R, Grundman R, Thomas R, Thal L. Donepezil and vitamin E as treatments for mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of Aging 2004;25(S2):20.
-
- Petersen RC, Thomas RG, Grundman M, Bennett D, Doody R, Ferris S, et al. Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;352(23):2379‐88. - PubMed
Thomas 2001 {published data only}
-
- Thomas A, Iacono D, Bonanni L, D' Andreamatteo G, Onofrj M. Donepezil, rivastigmine,and vitamin E in Alzheimer disease: a combined P300 event‐related potentials/neuropsychologic evaluation over 6 months. Clinical Neuropharmacology. US: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Inc., 2001; Vol. 24, issue 1:31‐42. - PubMed
Touchon 2006 {published data only}
-
- Touchon J, Bergman H, Bullock R, Rapatz G, Nagel J, Lane R. Response to rivastigmine or donepezil in Alzheimer's patients with symptoms suggestive of concomitant Lewy body pathology. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2006;22(1):49‐59. [PUBMED: 16393430] - PubMed
Tsolaki 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tsolaki M, Gerothanassis D, Aristotle CP. Efficacy and safety of cholinesterase inhibitors a longitudinal comparative study between donepezil and rivastigmine. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:2038.
Vanmechelen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Vanmechelen E, Andreasen N, Minthon L, Davidsson P, Amici S, Gallai V, et al. Effects of cholinesterase inhibitors on alzheimer disease biomarkers. Proceedings of the 7th International Geneva/Springfield Symposium on Advances in Alzheimer therapy, 2002 Apr 3‐6, Geneva 2002:252.
Wattmo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wattmo C, Hansson O, Wallin AK, Londos E, Minthon, L. Predicting long‐term cognitive outcome with new regression models in donepezil‐treated Alzheimer patients in a naturalistic setting.. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008;26(3):203‐11. - PubMed
Weiner 2000 {published data only}
-
- Weiner MF, Martin‐Cook K, Foster BM, Saine K, Fontaine CS, Svetlik DA. Effects of donepezil on emotional/behavioral symptoms in Alzheimer's disease patients. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2000a; Vol. 61, issue 7:487‐92. - PubMed
Werber 2002 {published data only}
-
- Werber EA, Klein C, Rabey MJ. Evaluation of cholinergic treatment in demented by p300 evoked related potentials. 8th conference on Alzheimer's disease and related disorders, July 20‐25, 2002, Stockholm, Sweden 2002:442.
Wilcock 2003 {published data only}
-
- Haworth J. Comparison of Aricept and galantamine (Reminyl) in Alzheimer's disease. National Research Register 2000.
-
- O'Brien A. A pilot study comparing the effect of galantamine (Reminyl) with donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's Disease. National Research Register 2000.
-
- Wilcock G, Howe I, Coles H, Lilienfeld S, Truyen L, Young Z, et al. and members of the GAL‐GBR‐2 Study Group. A long‐term comparison of galantamine and donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Drugs & Aging 2003;20(10):777‐89. - PubMed
Winstein 2007 {published data only}
-
- Winstein CJ, Bentzen KR, Boyd L, Schneider LS. Does the cholinesterase inhibitor, donepezil, benefit both declarative and non‐declarative processes in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease?. Current Alzheimer Research 2007;4(3):273‐76. - PubMed
Wyeth 2005 {published data only}
-
- Wyeth Research. A 3‐month, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, multicenter, safety, tolerability, and efficacy study of 3 doses of lecozotan (SRA‐333) SR in outpatients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease with donepezil as active control. ClinicalTrials.gov 2005.
Additional references
APA 1987
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd Edition. Washington DC: APA, 1987:American Psychiatric Association.
Berg 1988
-
- Berg L. Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR). Psychopharm Bull 1988;24:637‐9. - PubMed
Blau 1977
-
- Blau TH. Quality of life, social indicators and criteria of change. Professional Psychology 1977;8:464‐73.
Bucks 1996
-
- Bucks RS, Ashworth DL, Wilcock GK, Siegfried K. Assessment of activities of daily living in dementia: development of the Bristol Activities of Daily Living Scale. Age and Ageing 1996;25:113‐20. - PubMed
Chertkow 2013
Cohen‐Mansfield 1987
-
- Cohen‐Mansfield J, Marx MS, Rosenthal AS. A description of agitation in a nursinghome. Journal of Gerontology 1989;44:M77‐M84. - PubMed
Cummings 1994
-
- Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenburg‐Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J. The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 1994;44:2308‐13. - PubMed
Deeks 2017
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors) on behalf ofthe Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
DeJong 1989
-
- DeJong R, Osterlund OW, Roy GW. Measurement of quality‐of‐life changes in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Clinical Therapeutics 1989;11(4):545‐54. - PubMed
ECDEU 1976
-
- CGI Clinical Global Impressions. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. Publication ADM 76‐338. Rockville: US Dept of Health, Education and Welfare, 1976.
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein NF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini‐Mental State: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1975;12:189‐98. - PubMed
Galasko 2000
-
- Galasko D, Schmitt FA, Jin S. Detailed assessment of cognition and activities of daily living in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiology of Aging 2000;21(Suppl 1):S168. - PubMed
Goldberg 1988
-
- Goldberg DP, Williams P. A User's Guide to General Health Questionnaire. Windsor: NFER‐Nelson, 1988.
Gottfries 1982
-
- Gottfries CG, Brane G, Gullberg B, Steen G. A new rating scale for dementia syndromes. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 1982;1:311‐30. - PubMed
Gélinas 1999
-
- Gélinas I, Gauthier L, McIntyre M. Development of a functional measure for persons with Alzheimer's disease: the Disability Assessment for Dementia. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 1999;53:471‐81. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ (editors). Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2017
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Homma 1991
-
- Homma A, Niina R, Ishii T, Hasegawa K. Development of a new rating scale for dementia in the elderly: Mental Function Impairment Scale (MENFIS). Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1991;2:1217‐22.
ICD‐10
-
- World Health Organization. The ICD‐10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: clinical description and diagnostic guidelines. Geneva: World Health Organisation, Division of Mental Health, 1992.
Lawton 1969
-
- Lawton MP, Brody EM. Assessment of older people: self‐maintaining and instrumental activities of daily living. Gerontologist 1969;9:179‐86. - PubMed
Lee 2015
-
- Lee JH, Jeong SK, Kim BC, Park KW, Dash A. Donepezil across the spectrum of Alzheimer's disease: dose optimization and clinical relevance.. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2015;131(5):259‐67. - PubMed
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984;4:939‐44. - PubMed
Overall 1992
-
- Overall JE, Schaltenbrand R. The SKT neuropsychological test battery. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology 1992;5:220‐7. - PubMed
Panisset 1994
-
- Panisset M, Roudier M, Saxton J, Boller F. Severe Impairment Battery: a neurological test for severely demented patients. Archives of Neurology 1994;51:41‐5. - PubMed
Reisberg 1987
-
- Reisberg B, Borenstein J, Salob SP, Ferris SH, Franssen E, Georgotas A. Behavioral symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease: phenomenology and treatment. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1987;Suppl 48:9‐17. - PubMed
Ritchie 2017
-
- Ritchie CW, Russ TC, Banerjee S, Barber B, Boaden A, Fox NC, Holmes C, Isaacs JD, Leroi I, Lovestone S, Norton M, O'Brien J, Pearson J, Perry R, Pickett J, Waldman AD, Wong WL, Rossor MN, Burns A. The Edinburgh Consensus: preparing for the advent of disease‐modifying therapies for Alzheimer's disease.. Alzheimers Research & Therapy 2017;9:85. - PMC - PubMed
Rosen 1984
-
- Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis K. A new rating scale for Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Psychiatry 1984;141:1356‐64. - PubMed
Ryan 2015
-
- Ryan NS, Rossor MN, Fox NC. Alzheimer's disease in the 100 years since Alzheimer's death.. Brain 2015;138(Pt 12):3816‐21. - PubMed
Schneider 1997
-
- Schneider LS, Olin JT, Doody RS, et al. Validity and reliability of the Alzheimer's Disease Cooperative Study ‐ Clinical Global Impression of Change. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 1997;11(Suppl 2):S22‐32. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Schünemann 2017
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl E, et al. on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group and the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 11: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the confidence in or quality of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, Churchill R,Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Tan 2014
-
- Tan C‐C, Yu J‐T, Wang H‐F, Tan M‐S, Meng X‐F, Wang C, et al. Efficacy and safety of donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease 2014;41:615‐31. [DOI: 10.3233/JAD-132690] - DOI - PubMed
Wimo 1998
-
- Wimo A, Wetterholm AL, Mastey V, Winblad B. Evaluation of the healthcare resource utilization and caregiver time in anti‐dementia drug trials. In: Wimo A, Jönsson B, Karlsson G, Winblad B editor(s). Health Economics in Dementia. Chichester: Wiley, 1998:465‐77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

