Characteristics of Cobb angle distribution in the main thoracolumbar/lumbar curve in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A retrospective controlled clinical study
- PMID: 29924050
- PMCID: PMC6034568
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011216
Characteristics of Cobb angle distribution in the main thoracolumbar/lumbar curve in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A retrospective controlled clinical study
Abstract
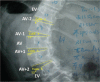
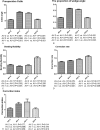
A single-center retrospective analysis of 46 patients with Lenke 5 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS).To compare Cobb angle distribution in different segments of the main thoracolumbar/lumbar curve in patients with Lenke 5 AIS, and differences in the lateral-bending flexibility, the correction rate, and correction index among these segments.No studies have been reported the ratio of the different segments to the main thoracolumbar/lumbar curve in terms of curve angle distribution, lateral-bending flexibility differences between these segments, and the correction rate when surgical instrumentations are used to correct scoliosis.Included in this study were 46 consecutive patients with Lenke 5 AIS. All of them received one-stage posterior correction and fusion with pedicle screw in the same center between January 2009 and January 2012. General data and radiological films before surgery, and at final follow-up were collected for further analysis. The wedging angles in the different discs were measured within main thoracolumbar/lumbar curve before and after surgery. This angle was also measured in the bending film. The preoperative flexibility, the correction rate, and the correction index of different disc segments were calculated.There were 44 (95.65%) female and 2 (4.35%) male included in this study, with the average age of 15.26 ± 2.19 years at the time of surgery. The mean Cobb angle was 45.09 ± 9.40°. The average disc wedge angles in AV - 2 (apex vetebrea-2), AV - 1, AV + 1, and AV + 2 segments were 5.59 ± 2.28°, 10.46 ± 3.41°, 9.85 ± 2.43°, 5.68 ± 2.80°, accounting for about 17.76%, 33.16%, 31.64%, and 17.44% of the Cobb angle in the main thoracolumbar/lumbar curve, respectively (P < .001). Flexibility of the supine lateral bending was 75.84%, 64.36%, 72.16% and 135.09% (P < .001), while the correction rates were 76.00%, 83.10%, 92.10%, and 109.65% (P < .001). The correction indexes were 1.16, 1.77, 2.02, and 1.11 for the disc of AV - 2, AV - 1, AV + 1, and AV + 2, respectively (P < .001).The disc angles are symmetric distribution in the main thoracolumbar/lumbar curve, and the distal segment is more flexible than the proximal/apical segments. Furthermore, the correction index is the highest in the apical vertebral segment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JC, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 2008;371:1527–37. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, Dang Y, Wu X, et al. Epidemiological study of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Eastern China. J Rehabil Med 2017;49:512–9. - PubMed
-
- Shufflebarger HL, King WF. Composite measurement of scoliosis: a new method of analysis of the deformity. Spine 1987;12:228–32. - PubMed
-
- Hopf C. [Criteria for treatment of idiopathic scoliosis between 40 degrees and 50 degrees. Surgical vs. conservative therapy]. Orthopade 2000;29:500–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

