Transcription Factor-Mediated Differentiation of Human iPSCs into Neurons
- PMID: 29924488
- PMCID: PMC6993937
- DOI: 10.1002/cpcb.51
Transcription Factor-Mediated Differentiation of Human iPSCs into Neurons
Abstract
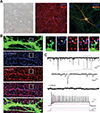
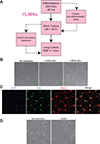
Accurate modeling of human neuronal cell biology has been a long-standing challenge. However, methods to differentiate human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to neurons have recently provided experimentally tractable cell models. Numerous methods that use small molecules to direct iPSCs into neuronal lineages have arisen in recent years. Unfortunately, these methods entail numerous challenges, including poor efficiency, variable cell type heterogeneity, and lengthy, expensive differentiation procedures. We recently developed a new method to generate stable transgenic lines of human iPSCs with doxycycline-inducible transcription factors at safe-harbor loci. Using a simple two-step protocol, these lines can be inducibly differentiated into either cortical (i3 Neurons) or lower motor neurons (i3 LMN) in a rapid, efficient, and scalable manner (Wang et al., 2017). In this manuscript, we describe a set of protocols to assist investigators in the culture and genetic engineering of iPSC lines to enable transcription factor-mediated differentiation of iPSCs into i3 Neurons or i3 LMNs, and we present neuronal culture conditions for various experimental applications. © 2018 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Keywords: i3LMN; i3Neurons; iPSC; iPSC-derived neurons; transcription factor-mediated differentiation.
Copyright © 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

