Association of protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 gene functional variant C1858T, HLA-DQ/DR genotypes and autoantibodies with susceptibility to type-1 diabetes mellitus in Kuwaiti Arabs
- PMID: 29924845
- PMCID: PMC6010291
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198652
Association of protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 gene functional variant C1858T, HLA-DQ/DR genotypes and autoantibodies with susceptibility to type-1 diabetes mellitus in Kuwaiti Arabs
Abstract
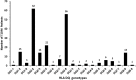
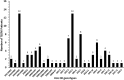
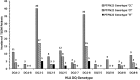
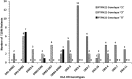
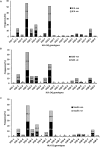
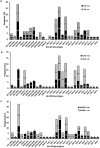
The incidence of type-1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) has increased steadily in Kuwait during recent years and it is now considered amongst the high-incidence countries. An interaction between susceptibility genes, immune system mediators and environmental factors predispose susceptible individuals to T1DM. We have determined the prevalence of protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 22 (PTPN22) gene functional variant (C1858T; R620W, rs2476601), HLA-DQ and DR alleles and three autoantibodies in Kuwaiti children with T1DM to evaluate their impact on genetic predisposition of the disease. This study included 253 Kuwaiti children with T1DM and 214 ethnically matched controls. The genotypes of PTPN22 gene functional variant C1858T (R620W; rs2476601) were detected by PCR-RFLP method and confirmed by DNA sequencing. HLA-DQ and DR alleles were determined by sequence-specific PCR. Three autoantibodies were detected in the T1DM patients using radio-immunoassays. A significant association was detected between the variant genotype of the PTPN22 gene (C1858T, rs2476601) and T1DM in Kuwaiti Arabs. HLA-DQ2 and DQ8 alleles showed a strong association with T1DM. In T1DM patients which carried the variant TT-genotype of the PTPN22 gene, 93% had at least one DQ2 allele and 60% carried either a DQ2 or a DQ8 allele. Amongst the DR alleles, the DR3-DRB5, DR3-3, DR3-4 and DR4-4 showed a strong association with T1DM. Majority of T1DM patients who carried homozygous variant (TT) genotype of the PTPN22 gene had either DR3-DRB5 or DRB3-DRB4 genotypes. In T1DM patients who co-inherited the high risk HLA DQ, DR alleles with the variant genotype of PTPN22 gene, the majority were positive for three autoantibodies. Our data demonstrate that the variant T-allele of the PTPN22 gene along with HLA-DQ2 and DQ8 alleles constitute significant determinants of genetic predisposition of T1DM in Kuwaiti children.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of interleukin-4, interleukin-13 gene polymorphisms, HLA-DQ and DR genotypes with genetic susceptibility of type-1 Diabetes Mellitus in Kuwaiti children.Front Pediatr. 2023 Apr 6;11:1118137. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1118137. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37090926 Free PMC article.
-
Risk genes and autoantibodies in Egyptian children with type 1 diabetes - low frequency of autoantibodies in carriers of the HLA-DRB1*04:05-DQA1*03-DQB1*02 risk haplotype.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015 Mar;31(3):287-94. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2609. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25256132
-
Genetic risk markers related to diabetes-associated autoantibodies in young patients with type 1 diabetes in berlin, Germany.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2010 Apr;118(4):245-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1246213. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20140847
-
Genetic prediction of autoimmunity: initial oligogenic prediction of anti-islet autoimmunity amongst DR3/DR4-DQ8 relatives of patients with type 1A diabetes.J Autoimmun. 2005;25 Suppl:40-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2005.09.002. Epub 2005 Oct 19. J Autoimmun. 2005. PMID: 16242305 Review.
-
Genetic susceptibility factors of Type 1 diabetes in Asians.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001 Jan-Feb;17(1):2-11. doi: 10.1002/1520-7560(2000)9999:9999<::aid-dmrr164>3.0.co;2-m. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11241886 Review.
Cited by
-
Fifty years of HLA-associated type 1 diabetes risk: history, current knowledge, and future directions.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 12;15:1457213. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1457213. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39328411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship of four vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with type 1 diabetes mellitus susceptibility in Kuwaiti children.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Mar 7;19(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1448-0. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30845908 Free PMC article.
-
Association between alleles, haplotypes, and amino acid variations in HLA class II genes and type 1 diabetes in Kuwaiti children.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 10;14:1238269. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1238269. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37638053 Free PMC article.
-
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) and Islet Autoantibodies Are Tools to Characterize Type 1 Diabetes in Arab Countries: Emphasis on Kuwait.Dis Markers. 2019 Nov 20;2019:9786078. doi: 10.1155/2019/9786078. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 31827651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Todd JA. Etiology of type 1 diabetes. Immunity. 2010;32:457–467. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.04.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sugihara S. Genetic susceptibility of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in Japan. Ped Endocrinol Rev. 2012;10:62–71. - PubMed
-
- Steck AK and Rewers MJ. Genetics of type 1 diabetes. Clin Chem. 2011;57;176–185. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.148221 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergholdt R, Brorsson C, Palleja A, Berchtold LA, Fløyel T, Bang-Berthelsen CH. et al. Identification of novel type 1 diabetes candidate genes by integrating genome-wide association data, protein-protein interactions and human pancreatic islet gene expression. Diabetes. 2012;61;954–962. doi: 10.2337/db11-1263 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

