Transcription Factor PU.1 Represses and Activates Gene Expression in Early T Cells by Redirecting Partner Transcription Factor Binding
- PMID: 29924977
- PMCID: PMC6063530
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.024
Transcription Factor PU.1 Represses and Activates Gene Expression in Early T Cells by Redirecting Partner Transcription Factor Binding
Erratum in
-
Transcription Factor PU.1 Represses and Activates Gene Expression in Early T Cells by Redirecting Partner Transcription Factor Binding.Immunity. 2018 Oct 16;49(4):782. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.09.019. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 30332634 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
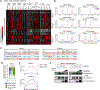
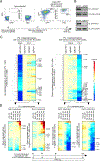
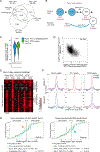
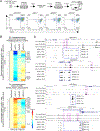
Transcription factors normally regulate gene expression through their action at sites where they bind to DNA. However, the balance of activating and repressive functions that a transcription factor can mediate is not completely understood. Here, we showed that the transcription factor PU.1 regulated gene expression in early T cell development both by recruiting partner transcription factors to its own binding sites and by depleting them from the binding sites that they preferred when PU.1 was absent. The removal of partner factors Satb1 and Runx1 occurred primarily from sites where PU.1 itself did not bind. Genes linked to sites of partner factor "theft" were enriched for genes that PU.1 represses despite lack of binding, both in a model cell line system and in normal T cell development. Thus, system-level competitive recruitment dynamics permit PU.1 to affect gene expression both through its own target sites and through action at a distance.
Keywords: DNA accessibility; Runx1; Satb1; Spi1; repression.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Transcription Factor Theft-PU.1 Caught Red-Handed.Immunity. 2018 Jun 19;48(6):1063-1065. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.05.007. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 29924967
References
-
- Cai Z, de Bruijn M, Ma X, Dortland B, Luteijn T, Downing RJ, and Dzierzak E. (2000). Haploinsufficiency of AML1 affects the temporal and spatial generation of hematopoietic stem cells in the mouse embryo. Immunity 13, 423-431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

