Platelet Signaling and Disease: Targeted Therapy for Thrombosis and Other Related Diseases
- PMID: 29925522
- PMCID: PMC6013590
- DOI: 10.1124/pr.117.014530
Platelet Signaling and Disease: Targeted Therapy for Thrombosis and Other Related Diseases
Abstract
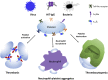
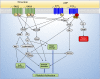
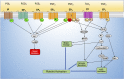
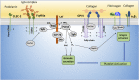
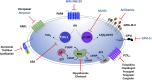
Platelets are essential for clotting in the blood and maintenance of normal hemostasis. Under pathologic conditions such as atherosclerosis, vascular injury often results in hyperactive platelet activation, resulting in occlusive thrombus formation, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Recent work in the field has elucidated a number of platelet functions unique from that of maintaining hemostasis, including regulation of tumor growth and metastasis, inflammation, infection, and immune response. Traditional therapeutic targets for inhibiting platelet activation have primarily been limited to cyclooxygenase-1, integrin αIIbβ3, and the P2Y12 receptor. Recently identified signaling pathways regulating platelet function have made it possible to develop novel approaches for pharmacological intervention in the blood to limit platelet reactivity. In this review, we cover the newly discovered roles for platelets as well as their role in hemostasis and thrombosis. These new roles for platelets lend importance to the development of new therapies targeted to the platelet. Additionally, we highlight the promising receptor and enzymatic targets that may further decrease platelet activation and help to address the myriad of pathologic conditions now known to involve platelets without significant effects on hemostasis.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Abramovitz M, Adam M, Boie Y, Carrière M, Denis D, Godbout C, Lamontagne S, Rochette C, Sawyer N, Tremblay NM, et al. (2000) The utilization of recombinant prostanoid receptors to determine the affinities and selectivities of prostaglandins and related analogs. Biochim Biophys Acta 1483:285–293. - PubMed
-
- Adili R, Tourdot BE, Mast K, Yeung J, Freedman JC, Green A, Luci DK, Jadhav A, Simeonov A, Maloney DJ, et al. (2017) First selective 12-LOX inhibitor, ML355, impairs thrombus formation and vessel occlusion in vivo with minimal effects on hemostasis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37:1828–1839. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey DE, Jr, Ganiats TG, Holmes DR, Jr, Jaffe AS, Jneid H, Kelly RF, Kontos MC, et al. ACC/AHA Task Force Members (2014a) 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines [published correction appears in Circulation (2014) 130:e433–e434]. Circulation 130:e344–e426. - PubMed
-
- Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey DE, Jr, Ganiats TG, Holmes DR, Jr, Jaffe AS, Jneid H, Kelly RF, Kontos MC, et al. ACC/AHA Task Force Members. Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (2014b) 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines [published correction appears in Circulation (2014) 130:e431–e432]. Circulation 130:2354–2394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

