Afatinib restrains K-RAS-driven lung tumorigenesis
- PMID: 29925635
- PMCID: PMC7610658
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aao2301
Afatinib restrains K-RAS-driven lung tumorigenesis
Abstract
On the basis of clinical trials using first-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), it became a doctrine that V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (K-RAS) mutations drive resistance to EGFR inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Conversely, we provide evidence that EGFR signaling is engaged in K-RAS-driven lung tumorigenesis in humans and in mice. Specifically, genetic mouse models revealed that deletion of Egfr quenches mutant K-RAS activity and transiently reduces tumor growth. However, EGFR inhibition initiates a rapid resistance mechanism involving non-EGFR ERBB family members. This tumor escape mechanism clarifies the disappointing outcome of first-generation TKIs and suggests high therapeutic potential of pan-ERBB inhibitors. On the basis of various experimental models including genetically engineered mouse models, patient-derived and cell line-derived xenografts, and in vitro experiments, we demonstrate that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved pan-ERBB inhibitor afatinib effectively impairs K-RAS-driven lung tumorigenesis. Our data support reconsidering the use of pan-ERBB inhibition in clinical trials to treat K-RAS-mutated NSCLC.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
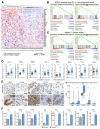
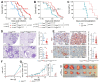
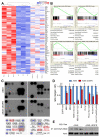


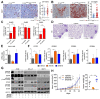
Comment in
-
Redefining KRAS activation.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018 Sep;15(9):532. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0068-1. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29985468 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Swanton C, Govindan R. Clinical Implications of Genomic Discoveries in Lung Cancer. The New England journal of medicine. 2016;374:1864–1873. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG, Halmos B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;352:786–792. - PubMed
-
- Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, Singh B, Heelan R, Rusch V, Fulton L, Mardis E, et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:13306–13311. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
