Does the Automatic Measurement of Interleukin 6 Allow for Prediction of Complications during the First 48 h of Acute Pancreatitis?
- PMID: 29925813
- PMCID: PMC6032432
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19061820
Does the Automatic Measurement of Interleukin 6 Allow for Prediction of Complications during the First 48 h of Acute Pancreatitis?
Abstract
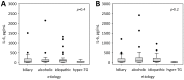
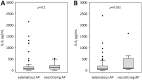
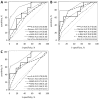
Acute pancreatitis (AP) in most patients takes a course of self-limiting local inflammation. However, up to 20% of patients develop severe AP (SAP), associated with systemic inflammation and/or pancreatic necrosis. Early prediction of SAP allows for the appropriate intensive treatment of severe cases, which reduces mortality. Serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been proposed as a biomarker to assist early diagnosis of SAP, however, most data come from studies utilizing IL-6 measurements with ELISA. Our aim was to verify the diagnostic usefulness of IL-6 for the prediction of SAP, organ failure, and need for intensive care in the course of AP using a fully automated assay. The study included 95 adult patients with AP of various severity (29 mild, 58 moderately-severe, 8 severe) admitted to a hospital within 24 h from the onset of symptoms. Serum IL-6 was measured using electochemiluminescence immunoassay in samples collected on admission and on the next day of hospital stay. On both days, patients with SAP presented the highest IL-6 levels. IL-6 correlated positively with other inflammatory markers (white blood cell and neutrophil counts, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin), the markers of renal injury (kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin), and the markers of endothelial dysfunction (angiopoietin-2, soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1). IL-6 on admission significantly predicted SAP, vital organ failure, and the need for intensive care or death, with areas under the receiver operating curve between 0.75 and 0.78, not significantly different from multi-variable prognostic scores. The fully automated assay allows for fast and repeatable measurements of serum IL-6, enabling wider clinical use of this valuable biomarker.
Keywords: acute pancreatitis; interleukin 6; organ failure; prediction of acute pancreatitis; severity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Goral V., Berekatoglu N., Mete N. Correlation of disease activity, IL-6 and CRP levels and leukocytes/lymphocyte ratio among patients with acute pancreatitis. J. Gastrointest. Dig. Syst. 2012;2:112. doi: 10.4172/2161-069X.1000112. - DOI
-
- Fukuda J.K., Franzon O., Resende-Filho F., Kruel N.F., Ferri T.A. Prognosis of acute pancreatitis by Panc3 Score. ABCD Arq. Brs. Cir. Dig. 2013;2:129–135. - PubMed
-
- Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines IAP/APA evidence guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2013;13:e1–e15. - PubMed
-
- Van Brunschot S., Schut A.J., Bouwerse S.A., Besselink M.G., Bakker O.J., van Goor H., Hofker S., Gooszen H.G., Boermeester M.A., van Santvoort H.C., et al. Abdominal compartment syndrome in acute pancreatitis. A systemic review. Pancreas. 2014;43:665–674. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000108. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

