Nuclear ARP2/3 drives DNA break clustering for homology-directed repair
- PMID: 29925947
- PMCID: PMC6145447
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0237-5
Nuclear ARP2/3 drives DNA break clustering for homology-directed repair
Abstract
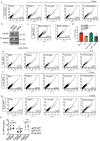
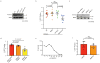
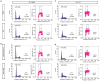
DNA double-strand breaks repaired by non-homologous end joining display limited DNA end-processing and chromosomal mobility. By contrast, double-strand breaks undergoing homology-directed repair exhibit extensive processing and enhanced motion. The molecular basis of this movement is unknown. Here, using Xenopus laevis cell-free extracts and mammalian cells, we establish that nuclear actin, WASP, and the actin-nucleating ARP2/3 complex are recruited to damaged chromatin undergoing homology-directed repair. We demonstrate that nuclear actin polymerization is required for the migration of a subset of double-strand breaks into discrete sub-nuclear clusters. Actin-driven movements specifically affect double-strand breaks repaired by homology-directed repair in G2 cell cycle phase; inhibition of actin nucleation impairs DNA end-processing and homology-directed repair. By contrast, ARP2/3 is not enriched at double-strand breaks repaired by non-homologous end joining and does not regulate non-homologous end joining. Our findings establish that nuclear actin-based mobility shapes chromatin organization by generating repair domains that are essential for homology-directed repair in eukaryotic cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests
Figures
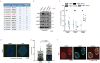
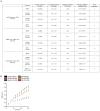
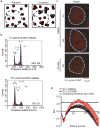


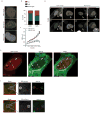

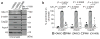





Comment in
-
Breakdancing on actin.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Aug;19(8):485. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0036-8. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29967438 No abstract available.
-
Breakdancing on actin.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Aug;19(8):469. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0033-y. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29967492 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

