Scents in the stack: olfactometric proficiency testing with an emission simulation apparatus
- PMID: 29926329
- PMCID: PMC6133125
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-018-2515-z
Scents in the stack: olfactometric proficiency testing with an emission simulation apparatus
Abstract
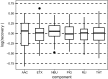
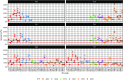
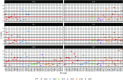
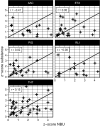
Olfactometry is globally acknowledged as a technique to determine odor concentrations, which are used to characterize odors for regulatory purposes, e.g., to protect the general public against harmful effects of air pollution. Although the determination procedure for odor concentrations is standardized in some countries, continued research is required to understand uncertainties of odor monitoring and prediction. In this respect, the present paper strives to provide answers of paramount importance in olfactometry. To do so, a wealth of measurement data originating from six large-scale olfactometric stack emission proficiency tests conducted from 2015 to 2017 was retrospectively analyzed. The tests were hosted at a unique emission simulation apparatus-a replica of an industry chimney with 23 m in height-so that for the first time, conventional proficiency testing (no sampling) with real measurements (no reference concentrations) was combined. Surprisingly, highly variable recovery rates of the odorants were observed-no matter, which of the very different odorants was analyzed. Extended measurement uncertainties with roughly 30-300% up to 20-520% around a single olfactometric measurement value were calculated, which are way beyond the 95% confidence interval given by the widely used standard EN 13725 (45-220%) for assessment and control of odor emissions. Also, no evidence has been found that mixtures of odorants could be determined more precisely than single-component odorants. This is an important argument in the intensely discussed topic, whether n-butanol as current reference substance in olfactometry should be replaced by multi-component odorants. However, based on our data, resorting to an alternative reference substance will not solve the inherent problem of high uncertainty levels in dynamic olfactometry. Finally, robust statistics allowed to calculate reliable odor thresholds, which are an important prerequisite to convert mass concentrations to odor concentrations and vice versa.
Keywords: EN 13725; Emission simulation apparatus; Odor threshold; Olfactometry; Proficiency test; Stack emission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Analytical Methods Committee Robust statistics-how not to reject outliers. Part 1. Basic concepts. Analyst. 1989;114:1693–1697. doi: 10.1039/AN9891401693. - DOI
-
- AS/NZS 4323.3 . Stationary source emissions-determination of odour concentration by dynamic olfactometry. Sydney: Australian and New Zealand Standards (AS/NZS); 2001.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

