Neurological complications of hematopoietic cell transplantation in children and adults
- PMID: 29926815
- PMCID: PMC6022482
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.233431
Neurological complications of hematopoietic cell transplantation in children and adults
Abstract
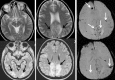
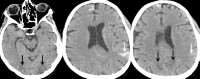
Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is widely performed for neoplastic and non-neoplastic diseases. HCT involves intravenous infusion of hematopoietic progenitor cells from human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-matched donor (allogeneic) or from the patient (autologous). Before HCT, the patient is prepared with high dose chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy to destroy residual malignant cells and to reduce immunologic resistance. After HCT, chemotherapy is used to prevent graft rejection and graft versus host disease (GvHD). Neurological complications are related to the type of HCT, underlying disease, toxicity of the conditioning regimens, immunosuppression caused by conditioning regimens, vascular complications generated by thrombocytopenia and/or coagulopathy, GvHD and inappropriate immune response. In this review, neurological complications are presented according to time of onset after HCT: (1) early complications (in the first month) - related to harvesting of stem cells, during conditioning (drug toxicity, posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome), related to pancytopenia, (2) intermediate phase complications (second to sixth month) - central nervous system infections caused by prolonged neutropenia and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy due to JC virus, (3) late phase complications (after sixth month) - neurological complications of GvHD, second neoplasms and relapses of the original disease.
Keywords: central nervous system infections; drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms; graft versus host disease; hematopoietic cell transplantation; immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; neurological complications; post-transplant acute limbic encephalitis; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; second neoplasm.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
-
Neurological complications of hematopoietic cell transplantation.Semin Neurol. 2004 Dec;24(4):427-34. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-861537. Semin Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15637654 Review.
-
Neurologic complications of hematopoietic cell transplantation.Semin Neurol. 2010 Jul;30(3):287-95. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1255218. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Semin Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20577935 Review.
-
Neurological complications of transplantation: part I: hematopoietic cell transplantation.Neurohospitalist. 2013 Jan;3(1):24-38. doi: 10.1177/1941874412455338. Neurohospitalist. 2013. PMID: 23983885 Free PMC article.
-
[Neurological complications of transplantation].Neurologia. 2008 Jul-Aug;23(6):373-86. Neurologia. 2008. PMID: 18597192 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Perspective: A Framework to Screen Pediatric and Adolescent Hematopoietic Cellular Therapy Patients for Organ Dysfunction: Time for a Multi-Disciplinary and Longitudinal Approach.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 24;11:622630. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.622630. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718184 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-engraftment neurological impairment in allogeneic stem cell transplant: A case report of atypical posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with pontine involvement.Front Transplant. 2023 Jan 25;1:1089995. doi: 10.3389/frtra.2022.1089995. eCollection 2022. Front Transplant. 2023. PMID: 38994387 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease, Infections, Vascular Events and Drug Toxicities Affecting the Central Nervous System.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 6;12:748019. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.748019. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34691059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoimmunity Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 25;11:2017. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02017. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation-Associated Neurological Complications and Their Brain MR Imaging Findings in a Pediatric Population.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 21;13(12):3090. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123090. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34205634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Airas L, Päivärinta M, Röyttä M, Karhu J, Kauppila M, Itälä-Remes M, Remes K. Central nervous system immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) after hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010;45:593–596. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong RJ, Elston JS, Hatton CS, Ebers GC. De novo relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis following autologous stem cell transplantation. Neurology. 2010;75:89–91. - PubMed
-
- Azik F, Yazal Erdem A, Tavil B, Bayram C, Tunc B, Uckan D. Neurological complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children, a single center experience. Pediatr Transplant. 2014;18:405–411. - PubMed
-
- Bauwens D, Hantson P, Laterre PF, Michaux L, Latinne D, De Tourtchaninoff M, Cosnard G, Hernalsteen D. Recurrent seizure and sustained encephalopathy associated with dimethylsulfoxide-preserved stem cell infusion. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46:1671–1674. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

