Enhancement of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 accompanied with neurogenesis following collagen glycosaminoglycan matrix implantation after surgical brain injury
- PMID: 29926827
- PMCID: PMC6022476
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.233443
Enhancement of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 accompanied with neurogenesis following collagen glycosaminoglycan matrix implantation after surgical brain injury
Abstract
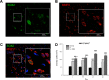
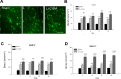
Surgical brain injury may result in irreversible neurological deficits. Our previous report showed that partial regeneration of a traumatic brain lesion is achieved by implantation of collagen glycosaminoglycan (CGM). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) may play an important role in neurogenesis but there is currently a lack of studies displaying the relationship between the stimulation of MMPs and neurogenesis after collagen glycosaminoglycan implantation following surgical brain trauma. The present study was carried out to further examine the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 after implantation of collagen glycosaminoglycan (CGM) following surgical brain trauma. Using the animal model of surgically induced brain lesion, we implanted CGM into the surgical trauma. Rats were thus divided into three groups: (1) sham operation group: craniotomy only; (2) lesion (L) group: craniotomy + surgical trauma lesion; (3) lesion + CGM (L + CGM) group: CGM implanted following craniotomy and surgical trauma lesion. Cells positive for SOX2 (marker of proliferating neural progenitor cells) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP2 and MMP9) in the lesion boundary zone were assayed and analyzed by immunofluorescence and ELISA commercial kits, respectively. Our results demonstrated that following implantation of CGM after surgical brain trauma, significant increases in MMP2+/SOX2+ cells and MMP9+/SOX2+ cells were seen within the lesion boundary zone in the L + CGM group. Tissue protein concentrations of MMP2 and MMP9 also increased after CGM scaffold implantation. These findings suggest that implantation of a CGM scaffold alone after surgical brain trauma can enhance the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 accompanied by neurogenesis.
Keywords: collagen glycosaminoglycan; matrix metalloproteinases; neural regeneration; neurogenesis; surgical brain trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Matrix Implantation following Surgical Brain Injury.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Jan 27;2019:6848943. doi: 10.1155/2019/6848943. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 30809107 Free PMC article.
-
Functional improvement and neurogenesis after collagen-GAG matrix implantation into surgical brain trauma.Biomaterials. 2012 Mar;33(7):2067-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.11.040. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22169139
-
Collagen-glycosaminoglycan matrix implantation promotes angiogenesis following surgical brain trauma.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:672409. doi: 10.1155/2014/672409. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25309917 Free PMC article.
-
Association of MMP2 and MMP9 gene polymorphisms with the recurrent spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2021 Jan 30;767:145173. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145173. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33007375 Review.
-
Prognostic values of tumoral MMP2 and MMP9 overexpression in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Feb 10;21(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-07860-2. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33568081 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine protects aged rats from postoperative cognitive dysfunction by alleviating hippocampal inflammation.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Sep;20(3):2119-2126. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10438. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31257507 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Matrix Implantation following Surgical Brain Injury.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Jan 27;2019:6848943. doi: 10.1155/2019/6848943. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 30809107 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

