Rho kinase inhibition maintains intestinal and vascular barrier function by upregulation of occludin in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis
- PMID: 29927318
- PMCID: PMC6230694
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00357.2017
Rho kinase inhibition maintains intestinal and vascular barrier function by upregulation of occludin in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis
Abstract
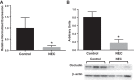
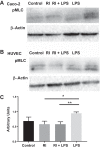
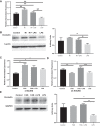
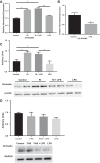
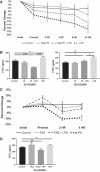
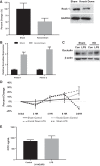
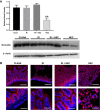
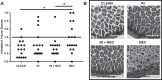
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a deadly disease that occurs in 5-10% of neonates. Although NEC has been extensively studied, no single therapeutic target has been identified. Rho kinase (ROCK) is a serine/threonine kinase that affects multiple cellular processes, including tight junction (TJ) function, cellular permeability, and apoptosis. We hypothesized that ROCK inhibition would decrease cellular permeability, stabilize TJ proteins (occludin), and decrease the severity of NEC. To test this hypothesis, human colon epithelial cells (Caco-2) and human endothelial cells were studied. Cells were treated with lipopolysaccharide to simulate an in vitro model of NEC. The effect of ROCK inhibition was measured by transepithelial membrane resistance (TEER) and cellular permeability to FITC-dextran. The effects of ROCK inhibition in vivo were analyzed in the rat pup model of NEC. NEC was induced by feeding formula supplemented with Cronobacter sakazakii with or without gavaged ROCK inhibitor. Rat intestines were scored based on histological degree of injury. RNA and protein assays for occludin protein were performed for all models of NEC. Treatment with ROCK inhibitor significantly decreased cellular permeability in Caco-2 cells and increased TEER. Intestinal injury scoring revealed decreased scores in ROCK inhibitor-treated pups compared with NEC only. Both cell and rat pup models demonstrated an upregulation of occludin expression in the ROCK inhibitor-treated groups. Therefore, we conclude that ROCK inhibition protects against experimental NEC by strengthening barrier function via upregulation of occludin. These data suggest that ROCK may be a potential therapeutic target for patients with NEC. NEW & NOTEWORTHY These studies are the first to demonstrate an upregulation of occludin tight junction protein in response to Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibition. Furthermore, we have demonstrated that ROCK inhibition in experimental models of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is protective against NEC in both in vitro and in vivo models of disease.
Keywords: Rho kinase inhibitors; necrotizing enterocolitis; occludin; tight junctions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caveolin 1 is Associated with Upregulated Claudin 2 in Necrotizing Enterocolitis.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 21;9(1):4982. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41442-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30899070 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK1 inhibitor stabilizes E-cadherin and improves barrier function in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Apr 1;318(4):G781-G792. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00195.2019. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32090605 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Bifidobacterium on Intestinal Barrier Function in LPS-Induced Enterocyte Barrier Injury of Caco-2 Monolayers and in a Rat NEC Model.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 23;11(8):e0161635. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161635. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27551722 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) and necrotizing enterocolitis.Semin Pediatr Surg. 2005 Aug;14(3):167-74. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2005.05.005. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2005. PMID: 16084404 Review.
-
Roles of nitric oxide and intestinal microbiota in the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis.J Pediatr Surg. 2016 Jan;51(1):13-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Pediatr Surg. 2016. PMID: 26577908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tight junctions: from molecules to gastrointestinal diseases.Tissue Barriers. 2023 Apr 3;11(2):2077620. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2022.2077620. Epub 2022 May 27. Tissue Barriers. 2023. PMID: 35621376 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory bowel disease risk gene C1ORF106 regulates actin dynamics in intestinal epithelial cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 15:2025.03.14.643205. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.14.643205. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40161582 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Small-molecule modulators of INAVA cytosolic condensate and cell-cell junction assemblies.J Cell Biol. 2021 Sep 6;220(9):e202007177. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202007177. Epub 2021 Jul 12. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34251416 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine alleviates enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced intestinal mucosal barrier function damage in a piglet model by modulation of the intestinal microbiome.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 14;11:1494348. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1494348. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39877539 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium exposure enhances VE-cadherin expression in endothelial cells via suppression of ROCK signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2022 May;23(5):355. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11282. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35481222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Khin S, Lieth E, Tarbell JM, Gardner TW; Penn State Retina Research Group . Vascular permeability in experimental diabetes is associated with reduced endothelial occludin content: vascular endothelial growth factor decreases occludin in retinal endothelial cells. Diabetes 47: 1953–1959, 1998. doi:10.2337/diabetes.47.12.1953. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

