Computational Analysis of Neonatal Mouse Ultrasonic Vocalization
- PMID: 29927553
- PMCID: PMC6055925
- DOI: 10.1002/cpmo.46
Computational Analysis of Neonatal Mouse Ultrasonic Vocalization
Abstract
Neonatal vocalization is structurally altered in mouse models of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Our published data showed that pup vocalization, under conditions of maternal separation, contains sequences whose alterations in a genetic mouse model of ASD impair social communication between pups and mothers. We describe details of a method which reveals the statistical structure of call sequences that are functionally critical for optimal maternal care. Entropy analysis determines the degree of non-random call sequencing. A Markov model determines the actual call sequences used by pups. Sparse partial least squares discriminant analysis (sPLS-DA) identifies call sequences that differentiate groups and reveals the degrees of individual variability in call sequences between groups. These three sets of analyses can be used to identify the otherwise hidden call structure that is altered in mouse models of developmental neuropsychiatric disorders, including not only autism but also schizophrenia. © 2018 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Keywords: Markov model; USV; autism spectrum disorder; entropy; mouse models; sPLS-DA; schizophrenia.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



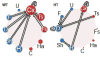
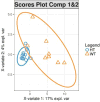
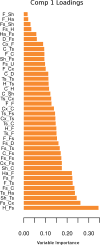
References
-
- Branchi I, Santucci D, Vitale A, Alleva E. Ultrasonic vocalizations by infant laboratory mice: a preliminary spectrographic characterization under different conditions. Dev. Psychobiol. 1998;33(3):249–256. - PubMed
-
- Bronson FH, Dagg CP, Snell GD. Reproduction. In: Green EL, editor. Biology of the Laboratory Mouse. Second. New York: Dover Publications, Inc.; 2007. Oneline publication). (Reprinted from: Not in File)
-
- Cierpial MA, Murphy CA, McCarty R. Maternal behavior of spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto normotensive rats: effects of reciprocal cross-fostering of litters. Behav. Neural Biol. 1990;54(1):90–96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

