Efficacy and safety of low-molecular-weight heparin after knee arthroscopy: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 29927930
- PMCID: PMC6013230
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197868
Efficacy and safety of low-molecular-weight heparin after knee arthroscopy: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is considered a potentially serious complication of knee arthroscopy and leads to conditions such as deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is widely employed in knee arthroscopy to reduce perioperative thromboembolic complications. However, the efficacy and safety of LMWH in knee arthroscopy remains unclear.
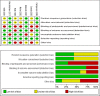
Methods: Seven randomized controlled clinical trials on LMWH in knee arthroscopy were identified and included in this meta-analysis. The main outcomes of the effectiveness (prevention of DVT and PE) and complications (death, major bleeding, and minor bleeding) of LMWH in knee arthroscopic surgery were assessed using Review Manager 5.3 software.
Results: The meta-analysis indicated that LMWH prophylaxis comprised 79% of asymptomatic DVT. No association was found in symptomatic VTE (RR: 0.90; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.39-2.08; P = 0.80), symptomatic DVT (RR: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.28-2.23; P = 0.66), symptomatic PE (RR: 1.36; 95% CI: 0.37-4.97; P = 0.64) and major bleeding (RR: 0.70; 95% CI: 0.12-3.95; P = 0.68) risk during LMWH prophylaxis were identified. Death was not reported in these studies. Moreover, there was a lower incidence of minor bleeding (RR: 0.64; 95% CI: 0.49 to 0.83; P = 0.001) in the control group than in the LMWH group.
Conclusion: Compared with the control group, the group treated with LMWH after knee arthroscopy was no association in reducing the symptomatic VTE rate, symptomatic DVT rate or symptomatic PE rate. The symptomatic VTE rate was 0.5% (11/2,166) in the LMWH group versus 0.6% (10/1,713) in the control group. Although the limitations of this meta-analysis cannot be ignored, the results of our study show that LMWH after knee arthroscopy is ineffective. We recommend that LMWH should not be routinely provided for knee arthroscopy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03164746.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

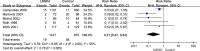





Similar articles
-
The effect of anticoagulants on venous thrombosis prevention after knee arthroscopy: a systematic review.Int Orthop. 2019 Oct;43(10):2303-2308. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4212-4. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Int Orthop. 2019. PMID: 30377699
-
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin for the Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients Undergoing Knee Arthroscopic Surgery and Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2019 Jul;47(8):1994-2002. doi: 10.1177/0363546518782705. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Am J Sports Med. 2019. PMID: 30113231
-
Prevention of venous thromboembolic events with low-molecular-weight heparin in the non-major orthopaedic setting: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Arthroscopy. 2014 Aug;30(8):987-96. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2014.03.009. Epub 2014 May 10. Arthroscopy. 2014. PMID: 24813323
-
The efficacy and safety of low-molecular-weight heparin in patients undergoing knee arthroscopic surgery and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 6;9(9):e19696. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19696. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37810025 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism after Arthroscopic Knee Surgery in a Low-Risk Population with the Use of Aspirin. A Randomized Trial.Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2015 Dec;73(4):243-8. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2015. PMID: 26630467 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
The effect of anticoagulants on venous thrombosis prevention after knee arthroscopy: a systematic review.Int Orthop. 2019 Oct;43(10):2303-2308. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4212-4. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Int Orthop. 2019. PMID: 30377699
-
Interventions for preventing venous thromboembolism in adults undergoing knee arthroscopy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 6;5(5):CD005259. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005259.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 22;8:CD005259. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005259.pub5. PMID: 32374919 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prophylaxis for preventing venous thromboembolism in knee arthroscopy and soft tissue reconstruction: consensus statements from an international panel of experts.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Nov;30(11):3634-3643. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-06973-w. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 35435469 Free PMC article.
-
Thromboprophylaxis after knee arthroscopy does not decrease the risk of deep vein thrombosis: a network meta-analysis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Jul;30(7):2364-2376. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06857-5. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 35112181
-
A rare case of pulmonary embolus after arthroscopic meniscus surgery.J Surg Case Rep. 2021 Apr 22;2021(4):rjab101. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjab101. eCollection 2021 Apr. J Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33936586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Adrichem RA, Nelissen RG, Schipper IB, Rosendaal FR,Cannegieter SC. Risk of venous thrombosis after arthroscopy of the knee: results from a large population-based case-control study. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(8):1441–8. doi: 10.1111/jth.12996 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Raskob GE, Angchaisuksiri P, Blanco AN, Buller H, Gallus A, Hunt BJ, et al. Thrombosis: a major contributor to the global disease burden. J Thromb Haemost.2014;12(10):1580–90. doi: 10.1111/jth.12698 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roth VP. Prophylaxis of deepvein thrombosis in outpatients undergoing arthroscopic meniscus operation. Orthop Prax.1995; 5:345–8.
-
- Wirth T, Schneider B, Misselwitz F, Lomb M, Tüylü H, Egbring R, et al.Prevention of venous thromboembolism after knee arthroscopy with low-molecular weight heparin (reviparin): Results of a randomized controlled trial. Arthroscopy. 2001;17(4):393–9. . - PubMed
-
- Michot M, Conen D, Holtz D, Erni D, Zumstein MD, Ruflin GB, et al. Prevention of deep-vein thrombosis in ambulatory arthroscopic knee surgery: A randomized trial of prophylaxis with low—molecular weight heparin. Arthroscopy. 2002;18(3):257–63. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

