Opposing roles of microRNA Argonautes during Caenorhabditis elegans aging
- PMID: 29927939
- PMCID: PMC6013023
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007379
Opposing roles of microRNA Argonautes during Caenorhabditis elegans aging
Abstract
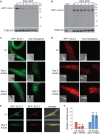
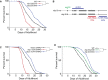
Argonaute (AGO) proteins partner with microRNAs (miRNAs) to target specific genes for post-transcriptional regulation. During larval development in Caenorhabditis elegans, Argonaute-Like Gene 1 (ALG-1) is the primary mediator of the miRNA pathway, while the related ALG-2 protein is largely dispensable. Here we show that in adult C. elegans these AGOs are differentially expressed and, surprisingly, work in opposition to each other; alg-1 promotes longevity, whereas alg-2 restricts lifespan. Transcriptional profiling of adult animals revealed that distinct miRNAs and largely non-overlapping sets of protein-coding genes are misregulated in alg-1 and alg-2 mutants. Interestingly, many of the differentially expressed genes are downstream targets of the Insulin/ IGF-1 Signaling (IIS) pathway, which controls lifespan by regulating the activity of the DAF-16/ FOXO transcription factor. Consistent with this observation, we show that daf-16 is required for the extended lifespan of alg-2 mutants. Furthermore, the long lifespan of daf-2 insulin receptor mutants, which depends on daf-16, is strongly reduced in animals lacking alg-1 activity. This work establishes an important role for AGO-mediated gene regulation in aging C. elegans and illustrates that the activity of homologous genes can switch from complementary to antagonistic, depending on the life stage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Comment in
-
The long and short of lifespan regulation by Argonautes.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jun 21;14(6):e1007415. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007415. eCollection 2018 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29927926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jonas S, Izaurralde E. Towards a molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16(7):421–33. doi: 10.1038/nrg3965 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli AE. MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(4):271–82. doi: 10.1038/nrg3162 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paul P, Chakraborty A, Sarkar D, Langthasa M, Rahman M, Bari M, et al. Interplay between miRNAs and Human Diseases: A Review. J Cell Physiol. 2017. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25854 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.246 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown KC, Svendsen JM, Tucci RM, Montgomery BE, Montgomery TA. ALG-5 is a miRNA-associated Argonaute required for proper developmental timing in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(15):9093–107. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx536 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5587817. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

