Genome-wide identification and comprehensive analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in Sesamum indicum
- PMID: 29927997
- PMCID: PMC6013105
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199262
Genome-wide identification and comprehensive analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in Sesamum indicum
Abstract
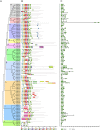
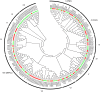
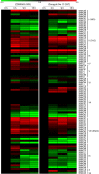
The NAM, ATAF1/2, and CUC2 (NAC) family constitutes a large family of plant-specific transcription factors, involved in many aspects of physiological processes and a variety of abiotic stresses. There is little information concerning the NAC family in Sesamum indicum. In this study, 87 sesame NAC genes were identified and phylogenetically clustered into 12 groups with Arabidopsis NAC genes. A total of 83 SiNAC genes were distributed non-randomly on the 16 linkage groups in sesame. Four and 49 SiNACs were found to be tandemly and segmentally duplicated, respectively. Expression profiles of SiNAC genes in different tissues (root, stem, leaf, flower, seed, and capsule) and in response to drought and waterlogging stresses by using RNA-seq data demonstrated that 23 genes were highly expressed in all tissues, 18 and 31 SiNACs respond strongly to drought and waterlogging stresses, respectively. In addition, the expression of 30 SiNAC genes distributed in different subgroups was analyzed with quantitative real-time RT-PCR under cold, osmotic, and salt stresses, revealed that their expression patterns vary in response to abiotic stresses. SiNAC genes displayed diverse expression patterns among the different tissues and stress treatments, suggested that their contribution to plant growth and development in sesame and multiple stress resistance in sesame. In this study, NAC transcription factors were analyzed in sesame and some specific candidate SiNAC genes in response to abiotic stress for functional study were identified. This study provides valuable information to deepen our understanding of the abiotic stress responses by NAC transcription factors in sesame.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of the HD-Zip gene family in response to drought and salinity stresses in sesame.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 16;20(1):748. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6091-5. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31619177 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of WRKY gene family in the sesame genome and identification of the WRKY genes involved in responses to abiotic stresses.BMC Plant Biol. 2017 Sep 11;17(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1099-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28893196 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the NAC Gene Family in Tea Plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze].PLoS One. 2016 Nov 17;11(11):e0166727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166727. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27855193 Free PMC article.
-
NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Feb;1819(2):97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22037288 Review.
-
Characteristics of NAC transcription factors in Solanaceae crops and their roles in responding to abiotic and biotic stresses.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 May 21;709:149840. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149840. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38564941 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Factors Associated with Abiotic and Biotic Stress Tolerance and Their Potential for Crops Improvement.Genes (Basel). 2019 Sep 30;10(10):771. doi: 10.3390/genes10100771. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31575043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome-wide and expression analysis of the NAC gene family in pepino (Solanum muricatum) during drought stress.PeerJ. 2021 Mar 29;9:e10966. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10966. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33850643 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide identification of NAC (no apical meristem/Arabidopsis transcription activation factor/cup-shaped cotyledon) transcription factors potentially involved in salt stress response in garlic.PeerJ. 2022 Dec 19;10:e14602. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14602. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36570011 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of the HD-Zip gene family in response to drought and salinity stresses in sesame.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 16;20(1):748. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6091-5. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31619177 Free PMC article.
-
Generating better leaf traits in M2 lines of fourteen Ethiopian sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genotypes through the treatment of their seeds with sodium azide.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 1;8(12):e11984. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11984. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36544826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyake Y, Fukumoto S, Okada M, Sakaida K, Nakamura Y, Osawa T. Antioxidative catechol lignans converted from sesamin and sesaminol triglucoside by culturing with Aspergillus. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2005;53(1):22–7. doi: 10.1021/jf048743h . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meshi T, Iwabuchi M. Plant transcription factors. Plant & cell physiology. 1995;36(8):1405–20. . - PubMed
-
- Puranik S, Sahu PP, Srivastava PS, Prasad M. NAC proteins: regulation and role in stress tolerance. Trends in plant science. 2012;17(6):369–81. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.02.004 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aida M, Ishida T, Fukaki H, Fujisawa H, Tasaka M. Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: an analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant. The Plant cell. 1997;9(6):841–57. doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.6.841 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mmadi MA, Dossa K, Wang LH, Zhou R, Wang YY, Cisse N, et al. Functional Characterization of the Versatile MYB Gene Family Uncovered Their Important Roles in Plant Development and Responses to Drought and Waterlogging in Sesame. Genes-Basel. 2017;8(12). doi: 10.3390/Genes8120362 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

