B-1 cells and B-1 cell precursors prompt different responses to Wnt signaling
- PMID: 29928002
- PMCID: PMC6013157
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199332
B-1 cells and B-1 cell precursors prompt different responses to Wnt signaling
Abstract
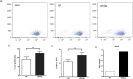
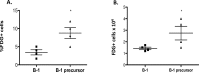
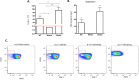
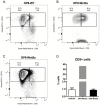
Recently several studies demonstrated a role for the Wnt pathway in lymphocyte development and self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). B-1 cells constitute a separate lineage of B lymphocytes, originating during fetal hematopoiesis, expressing lymphoid and myeloid markers and possessing self-renewal ability, similar to early hematopoietic progenitors and HSCs. A plethora of studies have shown an important role for the evolutionary conserved Wnt pathway in the biology of HSCs and T lymphocyte development. Our previous data demonstrated abundant expression of Wnt pathway components by B-1 cells, including Wnt ligands and receptors. Here we report that the canonical Wnt pathway is activated in B-1 cell precursors, but not in mature B-1 cells. However, both B-1 precursors and B-1 cells are able to respond to Wnt ligands in vitro. Canonical Wnt activity promotes proliferation of B-1 cells, while non-canonical Wnt signals induce the expansion of B-1 precursors. Interestingly, using a co-culture system with OP9 cells, Wnt3a stimulus supported the generation of B-1a cells. Taking together, these results indicate that B-1 cells and their progenitors are differentially responsive to Wnt ligands, and that the balance of activation of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling may regulate the maintenance and differentiation of different B-1 cell subsets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Montecino-Rodriguez E, Leathers H, Dorshkind K. Identification of a B-1 B cell-specified progenitor. Nat Immunol. 2006;7(3):293–301. Epub 2006/01/24. doi: 10.1038/ni1301 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dorshkind K, Montecino-Rodriguez E. Fetal B-cell lymphopoiesis and the emergence of B-1-cell potential. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(3):213–9. doi: 10.1038/nri2019 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yoshimoto M, Montecino-Rodriguez E, Ferkowicz MJ, Porayette P, Shelley WC, Conway SJ, et al. Embryonic day 9 yolk sac and intra-embryonic hemogenic endothelium independently generate a B-1 and marginal zone progenitor lacking B-2 potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(4):1468–73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015841108 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3029764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Montecino-Rodriguez E, Dorshkind K. B-1 B cell development in the fetus and adult. Immunity. 2012;36(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.017 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3269035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kantor AB, Herzenberg LA. Origin of murine B cell lineages. Annual review of immunology. 1993;11:501–38. Epub 1993/01/01. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.002441 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

